Vitamins can be divided into fat-soluble vitamins and water-soluble vitamins. Your body doesn’t store water-soluble vitamins. It rapidly removes them through urine. Hence, you need to consume sufficient amounts of these vitamins every day.
Vitamin B and C are the only water-soluble vitamins. Vitamin B can be further divided into eight vitamins. All the vitamins that fall under the category of vitamin B are coenzymes.
Food for thought: What are coenzymes?
A lot of chemical reactions happen in our bodies. Without these reactions, our survival would be impossible.
Enzyme
An enzyme is a macromolecule (a molecule made up of more than a hundred atoms). It acts as a catalyst (a helper) in chemical reactions like digestion and metabolism. However, these enzymes are highly selective catalysts, i.e., each enzyme acts as a catalyst only for a particular chemical reaction.
By reducing the energy needed to start these chemical reactions, enzymes speed up chemical reactions, up to a million times. In the absence of enzymes, some of these chemical reactions may not even happen.
Functions of enzymes:
Food: Enzymes help in breaking down the complex molecules in our food into smaller molecules like glucose, which provide instant energy.
DNA: Whenever a cell splits, the DNA it contains should be copied to the resulting daughter cells. Enzymes play a significant role in this process.
Toxins: Enzymes help the liver perform one of its primary functions – breaking down toxins in our bodies.
Proteins: Enzymes help break down proteins into amino acids, which are vital for many processes, including repairing cells after a workout.
Fats: Enzymes also help in breaking down fats, in our guts, into fatty acids. Fatty acids are absorbed into the bloodstream and used by the body for repairing cells, producing energy, and improving immunity.
Detergents: Enzymes are also used in many industries. One famous example is the use of enzymes in detergents to break down the proteins present in blood and egg.
During these processes, enzymes themselves are not consumed. Hence, once they finish catalyzing one chemical reaction, they can go and catalyze another similar chemical reaction.
Cofactors – To function properly, enzymes need cofactors. Cofactors help coenzymes function properly. There are two types of cofactors – coenzymes (organic – ions containing carbon) and inorganic ions (ions containing non-carbon atoms like Magnesium, Calcium, etc).
Coenzymes – Coenzymes can’t function alone. However, they attach themselves to enzymes so that the reacting molecules attach easily with the enzymes to form intermediate products.
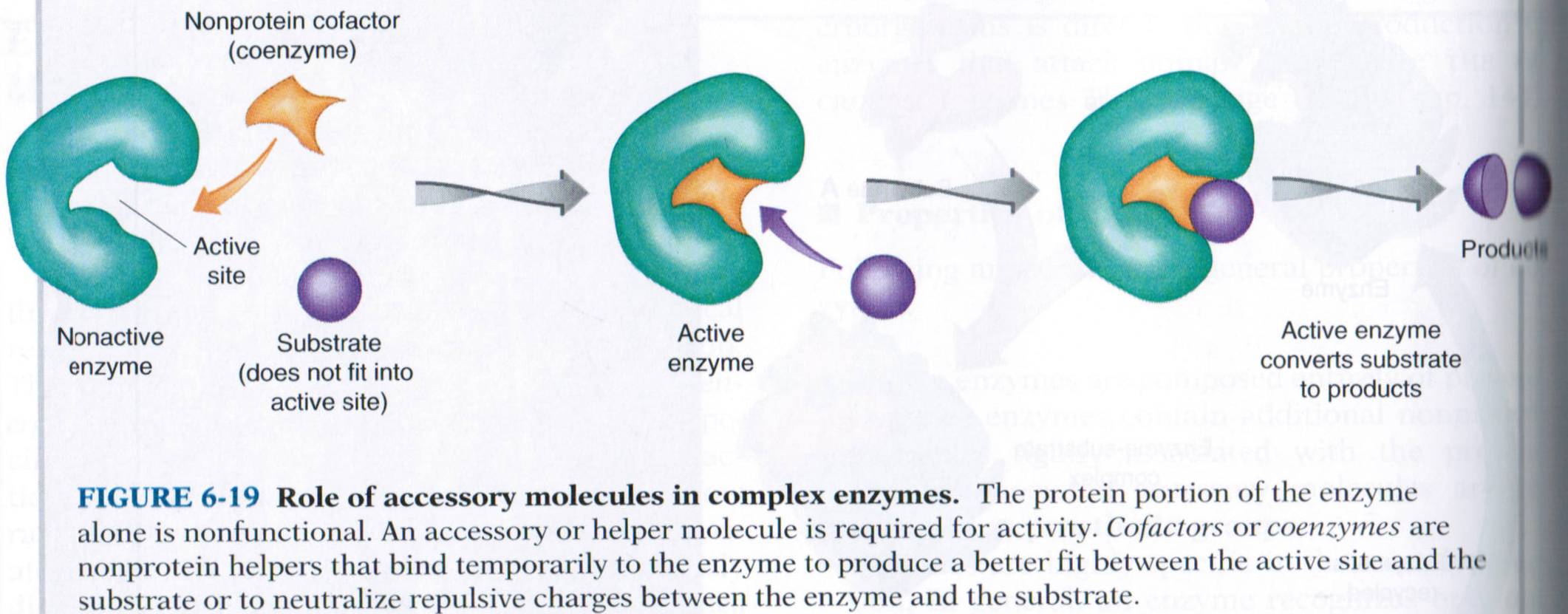
These intermediate products then react with other reacting molecules to form the final product and the enzyme. During this reaction, the shape of the coenzyme might change.
Reacting molecule 1 + Coenzyme = Intermediate product
Intermediate product + Reacting molecule 2 = Final product + Coenzyme
Coenzymes are essential to our bodies because they help enzymes perform chemical reactions easily and quickly.
Disclosure: While I have taken considerable efforts to make sure whatever written here is true, it cannot be guaranteed to be 100% accurate. This article is only meant to improve your knowledge of various vitamins and help you learn their functions and importance.
I advise you to do your research by following the links in the article and consulting your doctor or dietician before making any huge changes to your diet.
The approach used in this blog post
To understand the importance of vitamins, first, you will read the symptoms that occur due to its deficiency.
Then, you can try to identify the vitamin from these symptoms.
Once you have done that, you can go on to find the sources of that vitamin.
Then, you will find out who needs to take supplements of that vitamin, and how to help your body absorb that vitamin better.
If you want to read about fat-soluble vitamins, you can read my blog post here: Fat-soluble vitamins.
Identify this vitamin – 1
Among all the water-soluble vitamins, this is the first B vitamin that was discovered. It helps your body to convert carbohydrates into energy. The cells throughout your body, including those in your brain, use this energy.
It is involved in the creation of neurotransmitters that stimulate muscle control and behavior. These neurotransmitters are also essential for memory and cognition. Hence, the nervous system and the brain need this vitamin to function properly.

Deficiency
The deficiency of this water-soluble vitamin can cause fatigue and weakness (due to lack of energy) and can cause nerve damage (this vitamin helps in the creation of neurotransmitters, remember?).
It can lead to diseases like Beriberi (damage to the nervous system leading to muscular paralysis or damage to the cardiovascular system leading to heart failure). In extreme cases, it can cause Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome (damage to the brain leading to memory loss, hallucinations, etc.).
Overconsumption
Overdosing on this vitamin is extremely rare since your body excretes it through urine. Symptoms of rare cases of vitamin B1 supplement overdose can include diarrhea, allergic reactions, rapid heartbeat, etc.
Which vitamin is it?
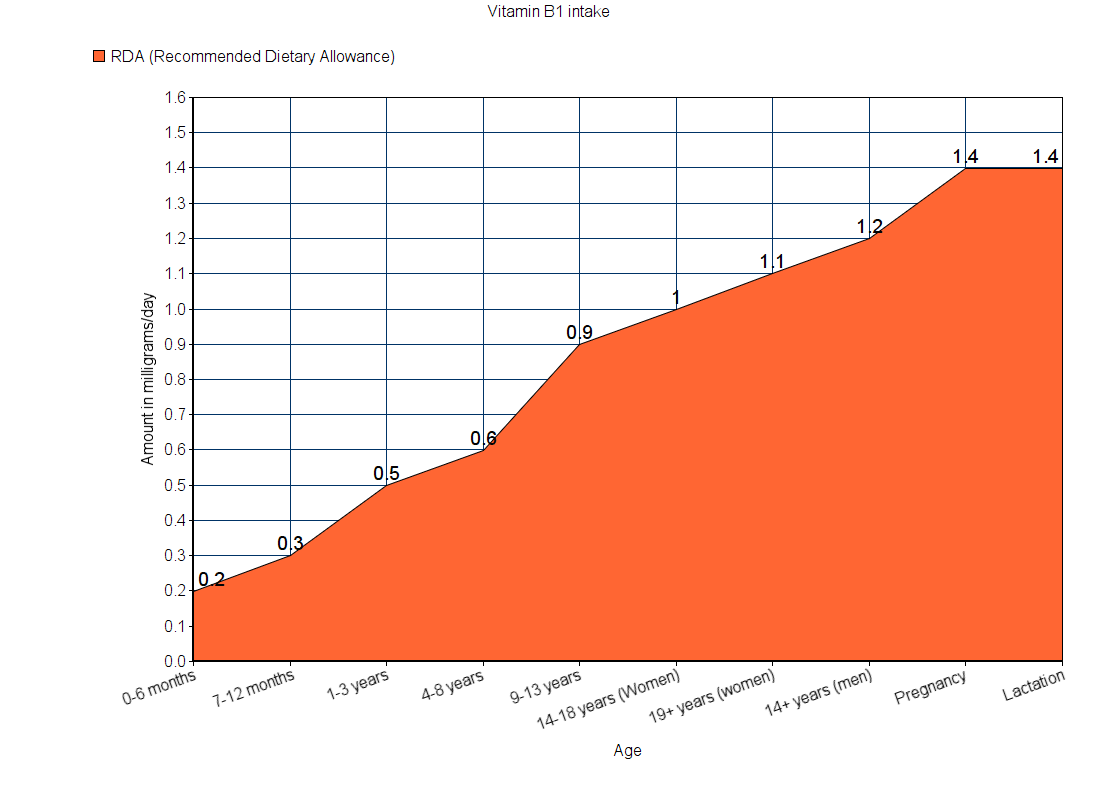
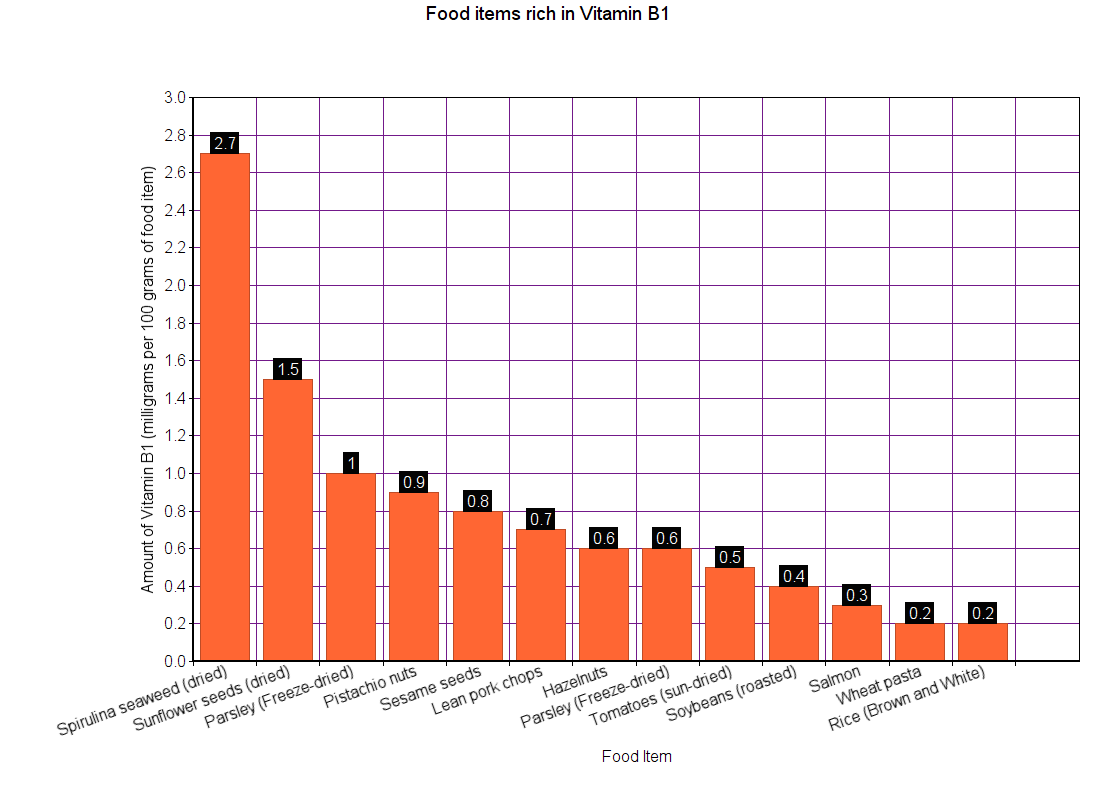
Vitamin B1 (Thiamine)
Sources
The Recommended Dietary Allowance for vitamin B1 is given in mg/day (milligrams per day). For infants less than a year old, RDA couldn’t be calculated. So, AI is used instead. Since vitamin B1 is not poisonous even when taken in high amounts, no UL data is available.
Note: All values are in milligrams
What are RDA, AI, and UL?
You can read the definitions for these terms here: Definitions of RDA, AI, and UL.
Best practices
How to absorb vitamin B1 effectively?
1. Vitamin B1 is a water-soluble vitamin. Your body can store it only for a short time. Then, your body removes it through the urine. So, you have to take it every day.
2. On cooking, 25% of the vitamin B1 is lost. So, using as little water as possible or using a microwave oven can reduce the amount of vitamin B1 lost through cooking.
Who should take supplements?
Healthy people normally don’t have a B1 deficiency. Hence, they don’t have to take vitamin B1 supplements.
1. People with high blood sugar levels are at risk of vitamin B1 deficiency because vitamin B1 is eliminated through urine. Vitamin B1 levels could be reduced by 75%-76% in these people. It is advisable for these people to either eat a B1 rich diet or take vitamin B1 supplements.
2. People who are chronic alcohol consumers are also at risk of vitamin B1 deficiency. While inadequate B1 intake is the main reason for this, high levels of alcohol can also impair B1 absorption as well as the conversion of B1 into coenzyme. These people can also benefit from vitamin B1 supplements.
3. Do not wash grains like rice in water if the packet doesn’t advise you to do so. Up to 25% of B1 is lost by washing rice once in the water.
How long does it take for your body to absorb the vitamin completely?
When you consume less than 5milligrams of vitamin B1, it can be absorbed almost immediately.
How long does the vitamin stay in the body?
While most of the vitamin B1 you consume is excreted within a day, a very small portion of it can remain for up to 3 days.
What happens to any excess of the vitamin you consume?
Your body can hold only a maximum of 30 milligrams of B1. Anything in excess is removed through the urine.
Food vs. supplements
The synthetic form of vitamin B1 is fat-soluble. Hence, it can be stored in your body for a longer time. However, this also makes it easier to overdose due to supplements.
Identify the vitamin – 2
Like other water-soluble vitamins, this vitamin helps in breaking down carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. It helps in the creation of red blood cells and recycling antioxidants.
It plays a significant role in maintaining healthy skin and good vision. Taking an adequate amount of this vitamin every day may also help prevent cataracts. It may also help reduce the number of migraine attacks. Taking supplements of this vitamin during a headache may reduce the pain experienced during migraines.
It helps convert other vitamins (B6 & B9) into forms that can be used by the body. It also impacts the absorption of other minerals (like iron) through the bloodstream.
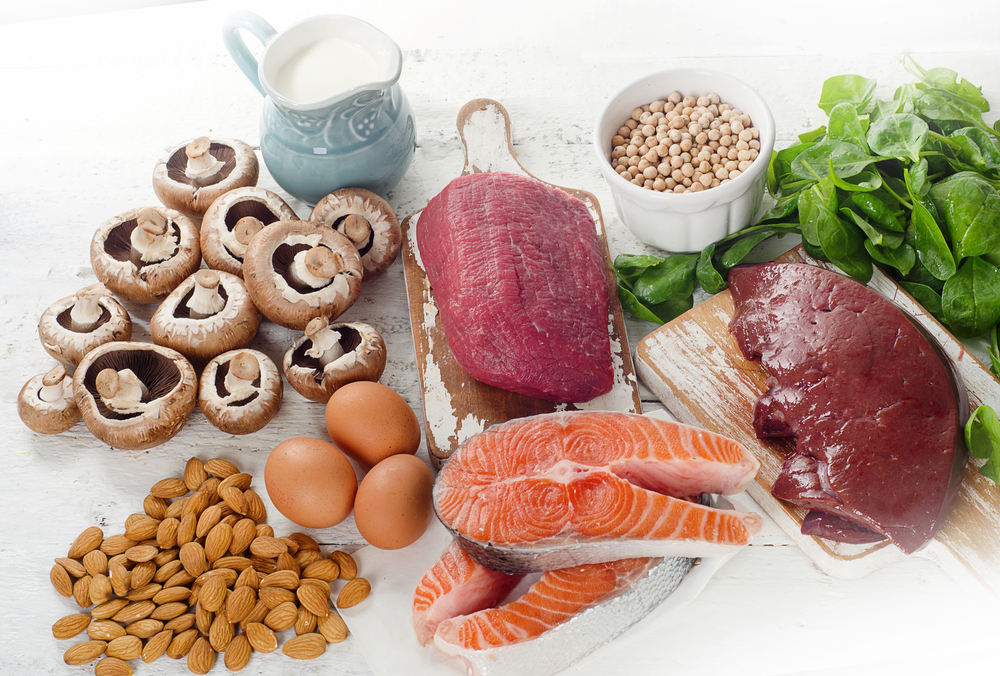

Deficiency
Since this vitamin is available in many common foods, it is rare for healthy people to have this deficiency. It may be caused due to a poor diet.
Also known as Ariboflavinosis, the reasons for this deficiency can be: primary (lack of this vitamin in the diet) or secondary (disability of the body to absorb the vitamin properly).
Due to its deficiency, several symptoms could show up within a few days. The tongue becoming red; Throat becoming sore; Corners of the mouth becoming swollen; Eyes becoming sensitive to light; Skin becoming dry and itchy on the nose and lips; Hair starting to fall; Rashes developing on the genitals, are some of those symptoms.
Since it impacts the absorption of iron in the body, its deficiency may also cause anemia, leading to a shortage of red blood cells.
Overconsumption
Excess of this vitamin is removed from the body through the urine. So, overconsumption of this vitamin doesn’t have any side-effects.
Only in extreme overdoses, it might cause diarrhea or yellowish-orange color of urine.
Which vitamin is it?
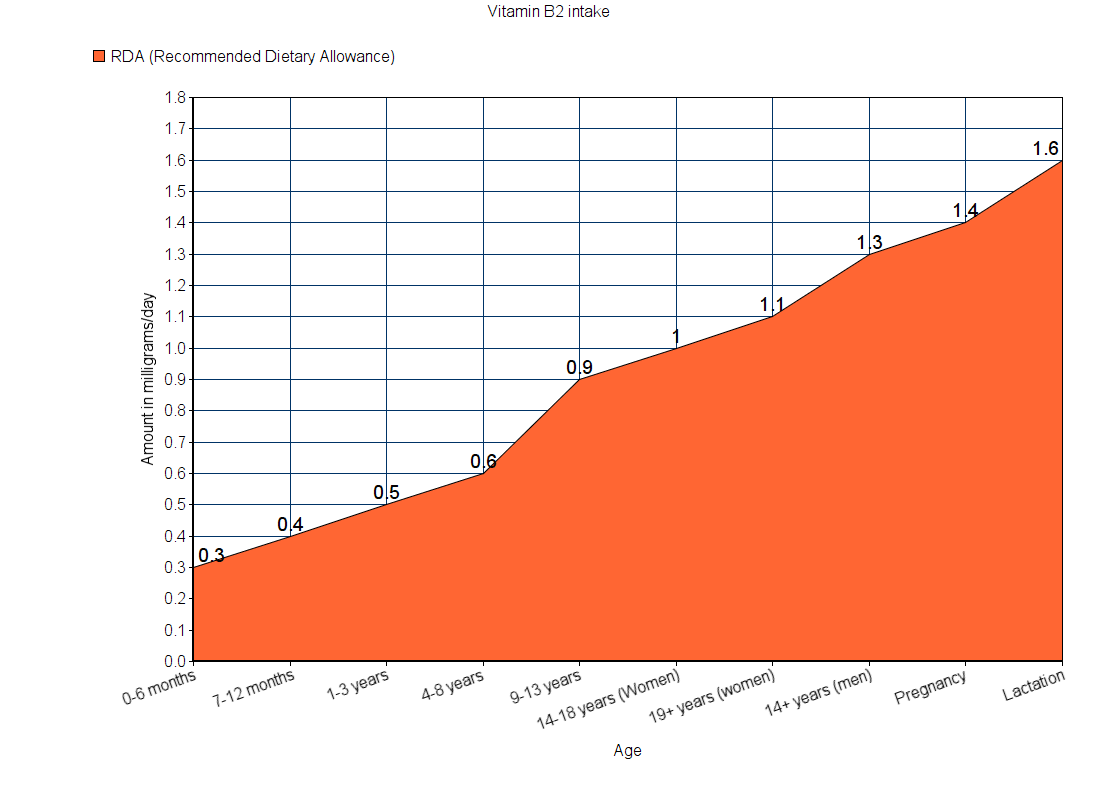
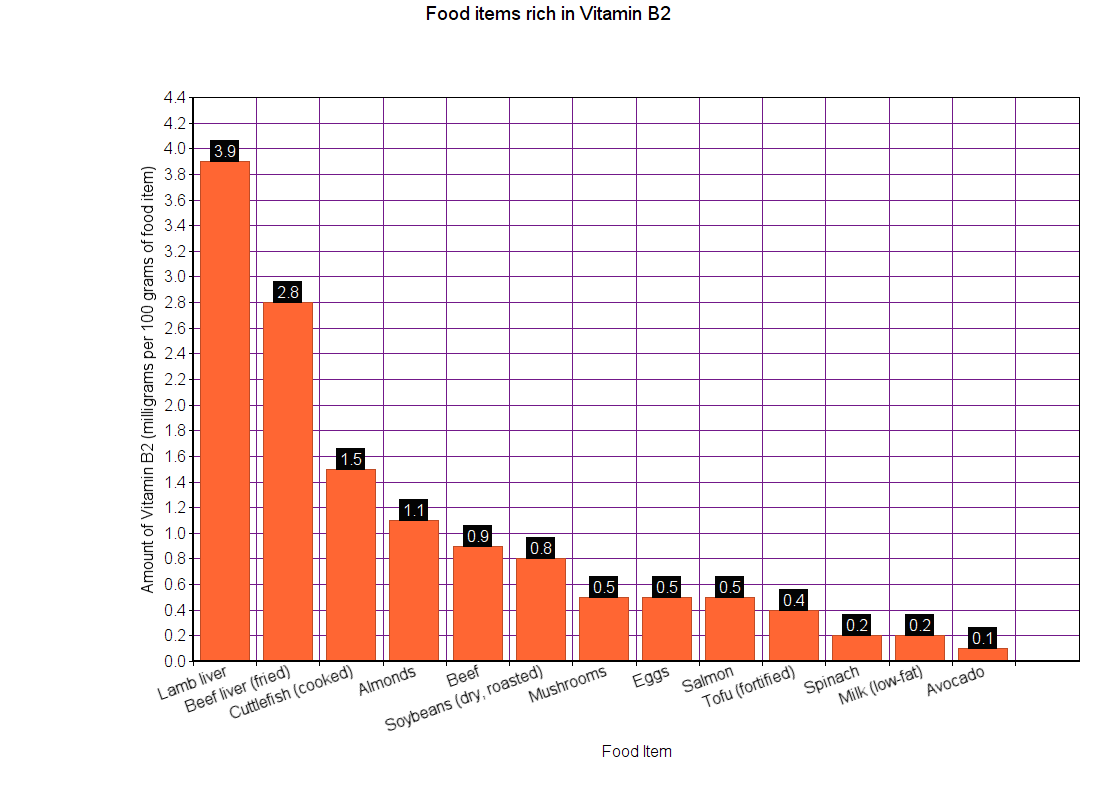
Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin)
Sources
Vitamin B2 is present in various food items. The RDA for children below one year is not known. Hence, AI is used.
Note: All values are in milligrams.
Best practices
How to absorb vitamin B2 better?
Water-soluble vitamins lose their nutrient value due to cooking.
However, vitamin B2 was believed to be the fraction of vitamin B that was most resistant to heat. But prolonged heating can still destroy its nutritional value. For example, milk loses up to 27% of its vitamin B2, when boiled for 15 minutes.
More than heat, light is the bigger enemy to vitamin B2. That is why milk comes mostly in opaque containers (paper or plastic).
To retain the vitamin B2 in the food you eat, store food items in a dark place. Eat fresh whenever possible. If you should cook, use as little water as possible, and drink the excess water after cooking.
Who should take supplements?
Normal healthy people don’t need to take supplements for water-soluble vitamins as deficiency is very rare in healthy people. This is true for vitamin B2 as well.
A poor diet and diseases that affect vitamin B2 absorption can cause vitamin B2 deficiency. It is more common in teenagers, older people, chronic alcoholics, and people with HIV.
Hence, these people may benefit from taking vitamin B2 supplements. Consuming even high doses of vitamin B2 is not toxic for healthy people. Hence, different doses of B2 are given to people depending on the intended benefit.
How much of the vitamin does your body absorb from your diet?
Your body can absorb nearly 100% of the vitamin B2 you eat.
How long does the vitamin stay in the body?
Like other B vitamins, it may remain in your body for 24 hours. Drinking lots of water can remove these vitamins faster due to the increased frequency of urination.
What happens to any excess of the vitamin you consume?
Excess vitamin B3 is not stored in your body. Instead, it is removed through urine rapidly.
Food vs. supplements
Natural forms of this vitamin are better absorbed and are safer to consume since toxicity due to overconsumption is rare. On the other hand, the safety of the synthetic forms has not been proven yet.
Identify the vitamin – 3
As a coenzyme, this vitamin is essential for digestion, energy production, and maintaining healthy skin and nerves.
This vitamin plays a vital role in cellular metabolism. It helps cells break down proteins, fats, and carbohydrates, as well as create enzymes and nucleic acids (remember DNA? ).
This vitamin helps in transporting oxygen to the cells and also helps cells communicate with each other. It acts as an antioxidant, protecting the cells in your body from oxidation by free radicals.
Its role in converting glucose into energy is also well known.
It helps in reducing the levels of bad cholesterol while increasing the levels of good cholesterol. So, it has been used as a major medication against cholesterol for the past 50 years. However, due to a study conducted in 2014, the efficiency of this vitamin against cholesterol has become highly disputed. Hence, it is not recommended as a medication against cholesterol anymore.
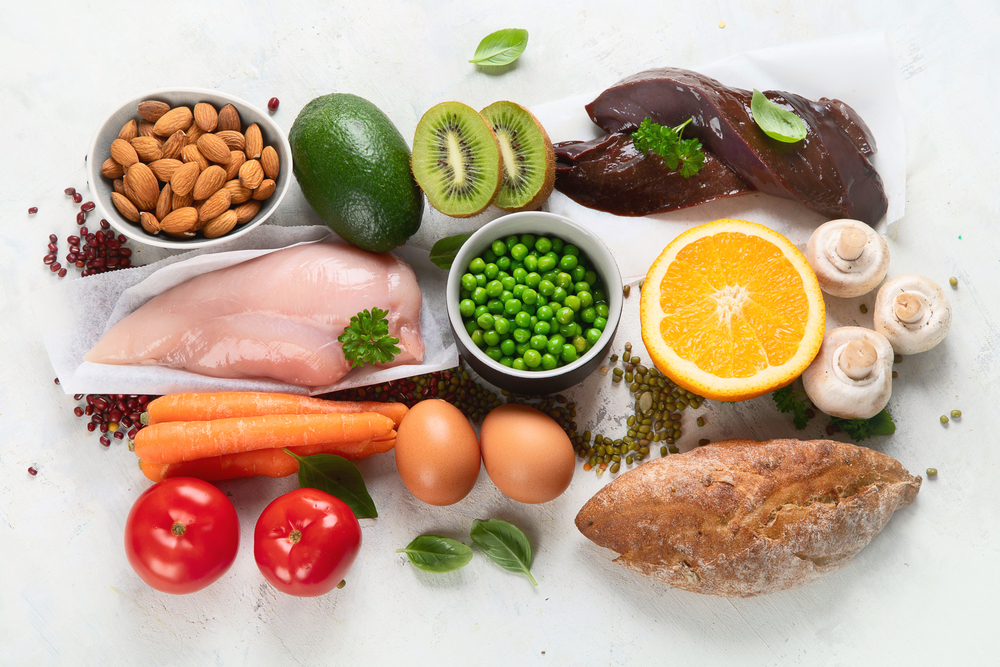

Deficiency
The deficiency of this vitamin is rare among healthy people but can occur in alcoholics.
Since it plays a role in digestion and energy production, mild deficiency can cause fatigue, indigestion, and vomiting. It can also cause headaches, mood swings, and depression.
Severe lack of this vitamin can cause Pellagra. Symptoms include flakey skin, digestion problems, diarrhea, loss of sleep, memory loss, and even mental impairment.
Since the body can produce this vitamin from an amino acid, a high-protein diet can prevent severe deficiency.
Overconsumption
Overdosing on this vitamin due to diet alone is not possible.
However, taking supplements can be harmful when taken in large quantities. Taking more than 1 gram/day can cause stomach upset, nausea (feeling like vomiting), and red, itchy skin to appear in the neck, chest, arms, and face. Taking 3-9 grams/day over an extended period can cause liver damage.
Which vitamin is it?
Vitamin B3 (Niacin)
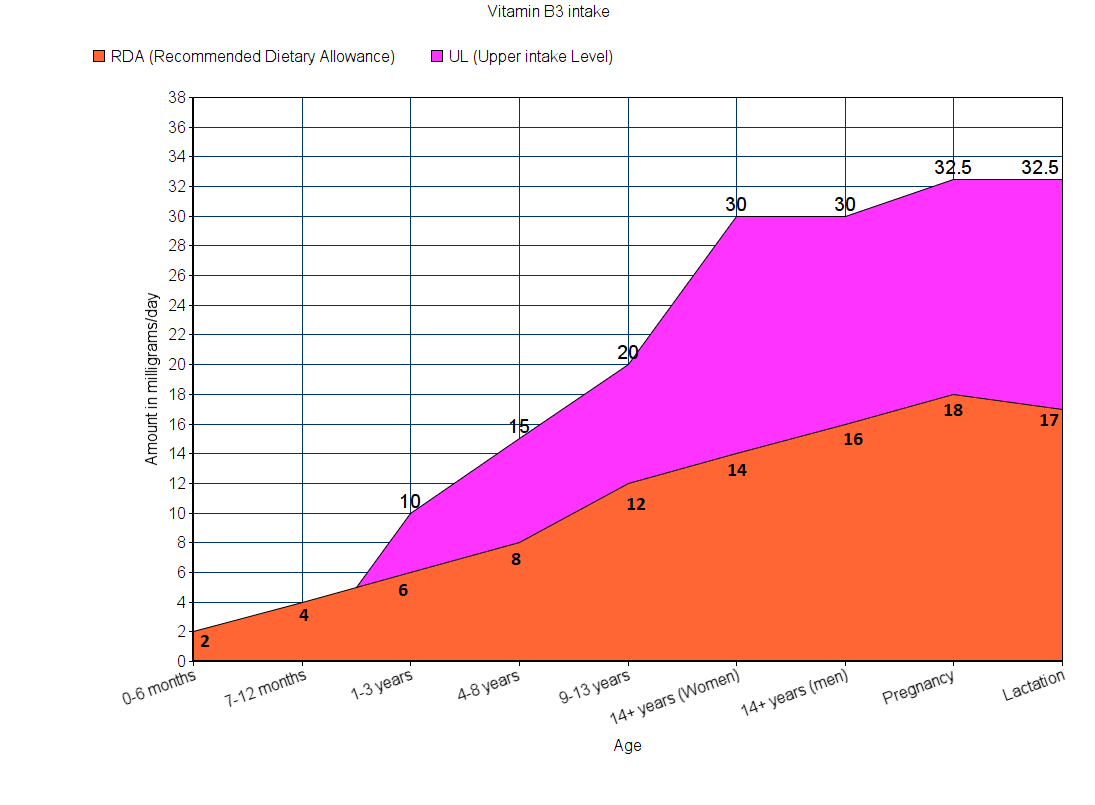
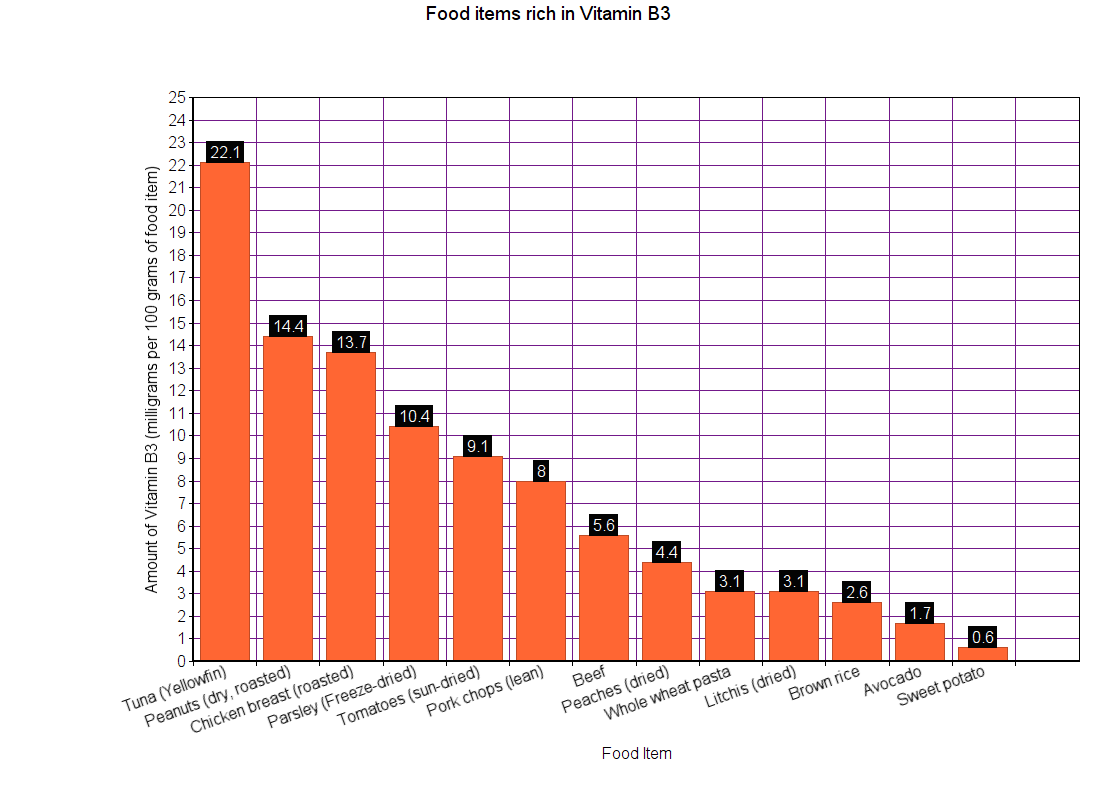
Sources
For children less than a year old, RDA amounts are not known. So, AI is used instead. The UL for these children are not known either.
Note: All values are in milligrams.
Best practices
How to absorb vitamin B3 better?
Like other B-vitamins, your body can absorb B3 better when you eat it with food. Protein-rich foods also provide a little bit of B3, provided B2, B6, and Magnesium are not lacking. So, eating protein-rich foods can help prevent severe cases of deficiency.
Who should take supplements?
Ordinary healthy people don’t need supplements since most of the foods, which people consume daily, are rich in vitamin B3. People belonging to the following categories may benefit from taking vitamin B3 supplements.
- Alcoholics
- Malnourished kids
- People eating low-calorie diets
- People eating diets containing refined carbohydrates
- Mothers who nurse more than one baby
- People suffering from inflammatory bowel disease
- People having vitamin B2, B6, iron or Magnesium deficiency
However, since vitamin B3 overdose can be deadly, it is advisable to consult a doctor before buying supplements.
How long does it take for your body to absorb the vitamin completely?
Like other B vitamins, vitamin B3 can be absorbed quickly(within 24 hours).
How long does the vitamin stay in the body?
Most of the vitamin B3 you consume is excreted within 24 hours.
What happens to any excess of the vitamin you consume?
Any excess vitamin B3 you consume is removed through the urine.
Food vs. supplements
Synthetic forms of vitamin B3 are found to have better absorption rates than B3 in natural sources.
Identify the vitamin – 4
This vitamin is found in almost all food items. Indeed, it got its name from the Greek word ‘Pantothen,’ which means ‘from everywhere.’ On the contrary, it is also one of the lesser-known vitamins because its deficiency is rare.
It is vital for many chemical reactions that happen in your body. Like other B-vitamins, it helps in creating energy from carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, and in maintaining a healthy digestive system. It also helps in producing red blood cells, sex- and stress-related hormones, neurotransmitters, and in processing other vitamins (B2).
Its most important use is in synthesizing Coenzyme A. Coenzyme A helps the body in creating fatty acids and cholesterol from food. The liver also needs Coenzyme A for breaking down toxins and drugs.
Supplements of this vitamin are taken to reduce cholesterol.
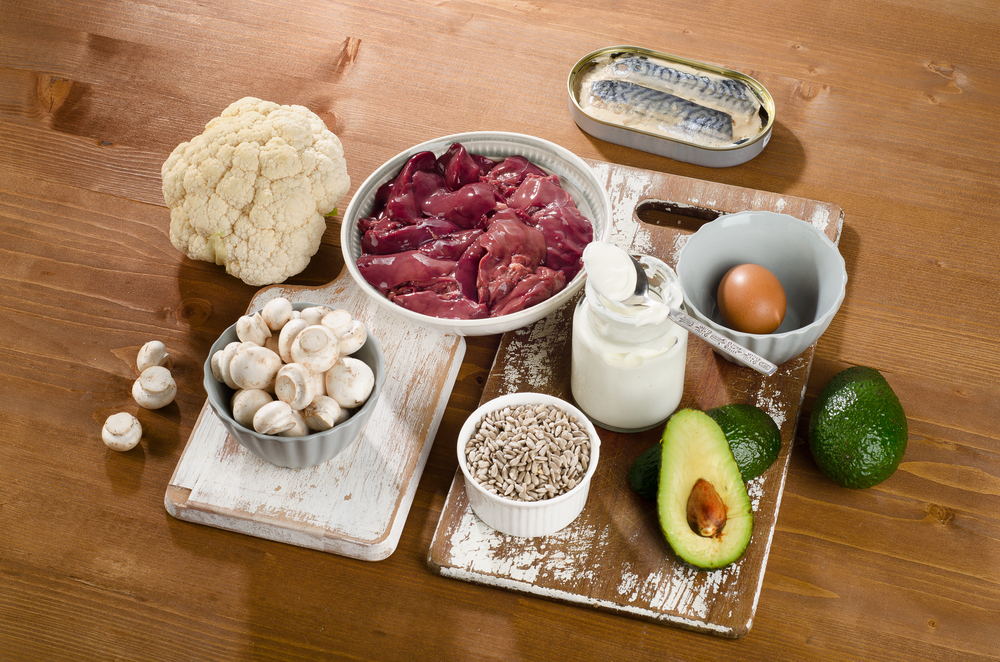

Deficiency
The deficiency of this vitamin is extremely rare since it is found in almost all the food items. It can occur as a result of severe malnutrition and can affect many organs. Symptoms include vomiting, stomach pain, numbness, cramps, skin irritation, sleeping disorders, and depression.
Overconsumption
This vitamin, when taken through food, is completely safe. For this reason, it doesn’t have an upper limit. It causes diarrhea when taken in high amounts (10-20 g).
However, taking it as a supplement is a completely different story.
Which vitamin is it?
Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic acid )
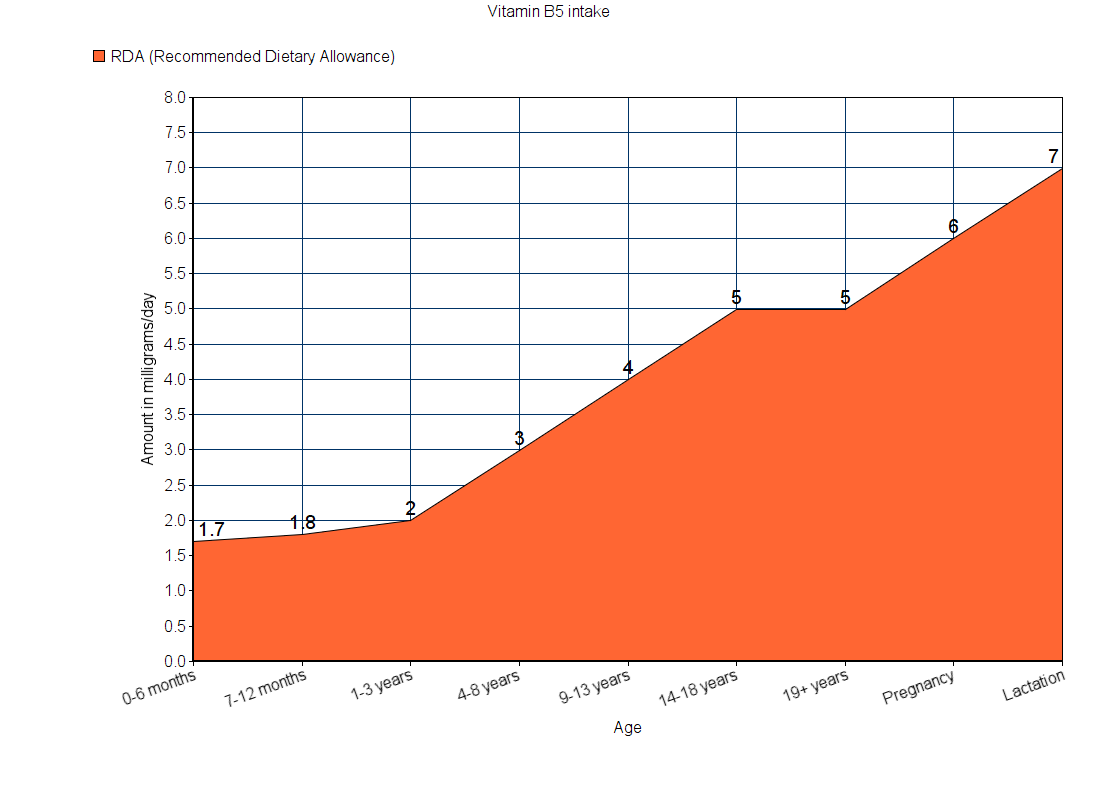
Sources
The graphs below show the RDA data for B5, as well as the amount of vitamin B5 contained in different food items.
Note: All values are in milligrams
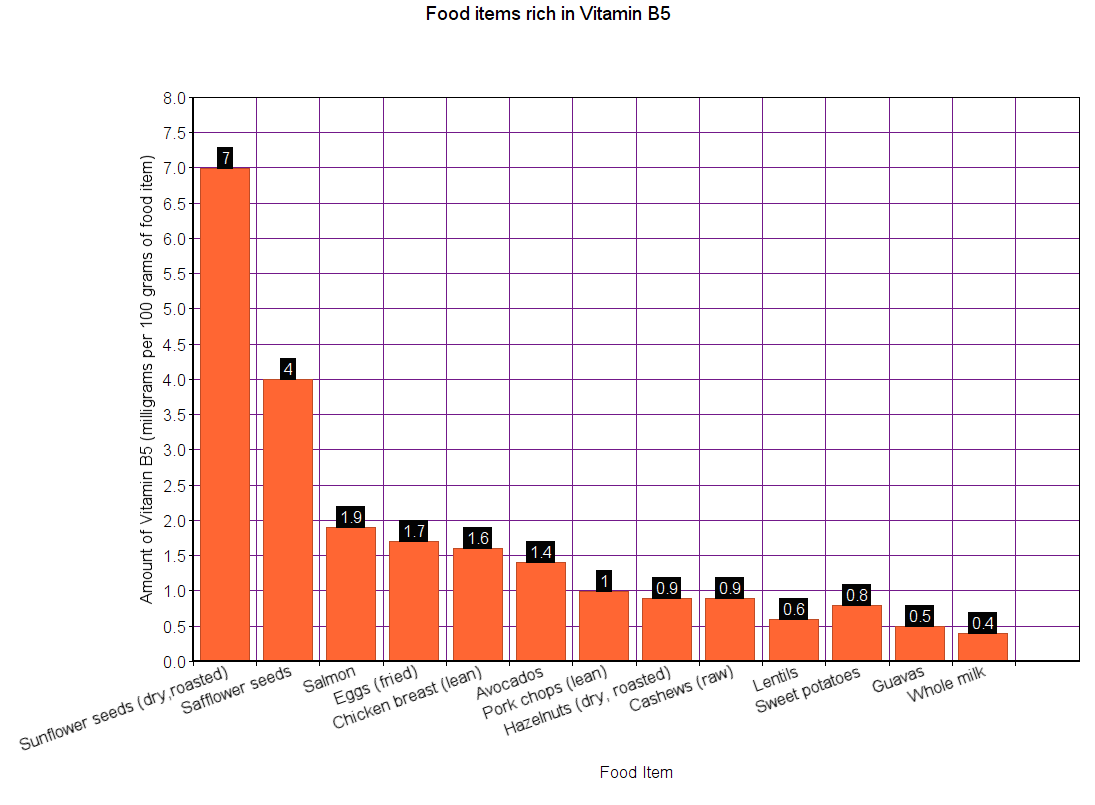
Best practices
How to absorb vitamin B5 better?
Since other nutrients support the absorption of vitamin B5, eat it along with food. If you take supplements, take multivitamin supplements, instead of B5 supplements. Since heat can destroy vitamin B5, try to eat as many raw sources of B5 as possible.
Who should take supplements?
People who consume alcohol excessively or have Diabetes may need higher amounts of vitamin B5. Hence, taking supplements can benefit them greatly.
Care should be taken while taking vitamin B5 supplements since it can interfere with medications. For example, people taking blood-thinning medicines should not take B5 supplements, as it can increase the risk of bleeding. So, consult your doctor before taking vitamin B5 supplements.
How long does it take for your body to absorb the vitamin completely?
Your body can absorb almost 100% of the vitamin B5 within 24 hours.
How long does the vitamin stay in the body?
Your body excretes almost all of the vitamin B5 within the first 24 hours of consumption.
What happens to any excess of the vitamin you consume?
Vitamin B5 is one of the safest water-soluble vitamins. Your body removes any excess amount you consume by urination.
Food vs. supplements
Synthetic forms of vitamin B5 are easily available and are cheaper than natural food sources. Other than that, there aren’t any other advantages to taking supplements.
Read the rest of the blog post here: Water-soluble vitamins Part 2