Do you know what the four fat-soluble vitamins are and why your body needs these vitamins? Do you know how to identify if you lack any of these vitamins? If you don’t know, do not fret. This blog post will tell you everything you need to know.
There is an ancient Indian proverb that says food is medicine.
Our ancestors lived a life proving that it is true. By eating a balanced diet rich in proteins, healthy fats, carbohydrates, essential vitamins, and minerals, they lived healthily.
Many of us, however, have forgotten the importance and the source of vitamins vital to our survival.
Vitamins are named in the order of their discovery, starting from ‘A’ going all the way to ‘E’. The only exception is vitamin ‘K’, which was assigned ‘K’ from ‘Koagulation’ by its Danish researcher.
In a blog post like this, the usual approach is to list the vitamins, their sources, and their importance. However, in this blog post, I have used a different approach.
To understand the importance of vitamins, first, you will read the symptoms that occur due to its deficiency.
Then, you can try to identify the vitamin from these symptoms.
Once you have done that, you can go on to find the sources of that vitamin.
Then, you will find out who needs to take supplements of that vitamin, and how to help your body absorb that vitamin better.
Disclosure: While I have taken considerable efforts to make sure whatever written here is true, it cannot be guaranteed to be 100% accurate. This article is only meant to improve your knowledge of various vitamins and help you learn their functions and importance.
I advise you to do your research by following the links in the article and consulting your doctor or dietician before making any huge changes to your diet.
Types of vitamins
Vitamins are classified into two types: Fat-soluble and Water-soluble.
Water-soluble vitamins
Water-soluble vitamins, like the name indicates, are soluble in water. The tissues in your body can easily absorb these vitamins. However, Your body uses these vitamins immediately and does not store them for later use. So, you have to regularly consume these vitamins in small doses.
Overconsumption of water-soluble vitamins is not harmful to the body since your body excretes any excess vitamins through urine.
If you want to read about water-soluble vitamins, read our blog post here: Water-soluble vitamins.
Fat-soluble vitamins
Fat-soluble vitamins, on the other hand, are like oil and are not soluble in water. The bloodstream in your body distributes them throughout the body and your liver and fatty tissues store them for later use. The body absorbs these vitamins better when eaten along with fats.
Overconsumption of fat-soluble vitamins can lead to the creation of poisonous chemicals in the body.
Definitions:
RDA
The Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) refers to the average daily amount of a vitamin that is sufficient to meet the nutrient requirements of 97% – 98% of healthy people of a particular age, sex, physiological condition, or life stage. It is used for planning your diet.
AI:
Whenever RDA cannot be determined, an Adequate Intake (AI) is used. It is also a recommended average daily intake level. However, unlike RDA, it is not accurate. AI is based on approximations of nutrient intake by groups of healthy people that are observed, estimated, or experimentally determined and are assumed to be adequate.
UL:
The Upper Intake Level (UL) is the maximum amount of nutrients a person in the general population can consume, without exposing himself/herself to any risk of adverse health effects.
Identify this fat-soluble vitamin – 1
It is a fat-soluble vitamin needed for good vision and maintaining the health of your bones.
It helps in creating and distributing T-cells, a type of white blood cells, throughout the body. Therefore, it improves the immunity of the body.
It is important for cell growth. Hence, it plays an important role in keeping the skin cells healthy.
It is also involved in the development of sperms and eggs. Hence, it is needed for reproduction.

Deficiency
Since this fat-soluble vitamin is stored in the liver for years, it might take two years for the symptoms of this deficiency to show up.
Eyes becoming dry is one of the first symptoms of deficiency of this vitamin.
Eye-related problems are some of the most common effects of deficiency of this vitamin.
Lack of this vitamin can also lead to dry skin, poor healing, reduced growth, and infertility. It is more common in African nations where malnutrition is prevalent.
Overconsumption
Overconsumption of this vitamin can lead to mouth ulcers, rough skin, vision changes, and birth defects in pregnant women. Hence, it is better to consult your doctor before taking vitamin supplements.
Which vitamin is it?
Vitamin A, also known as Retinol.
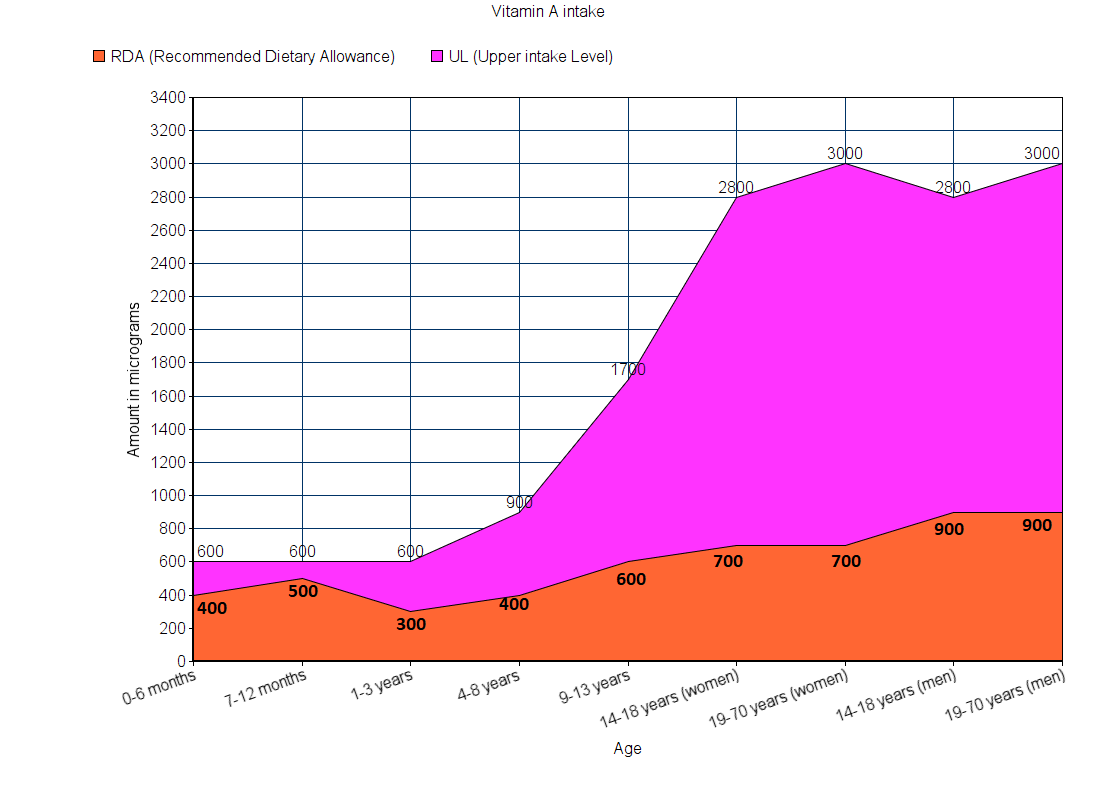
How much should you consume every day
The intake of vitamin A varies depending on the age of the person. The graph below gives you an idea of the Recommended Dietary Allowance and the Upper intake Limit per day for infants, children, women, and men of all ages.
Note: All values are in micrograms.
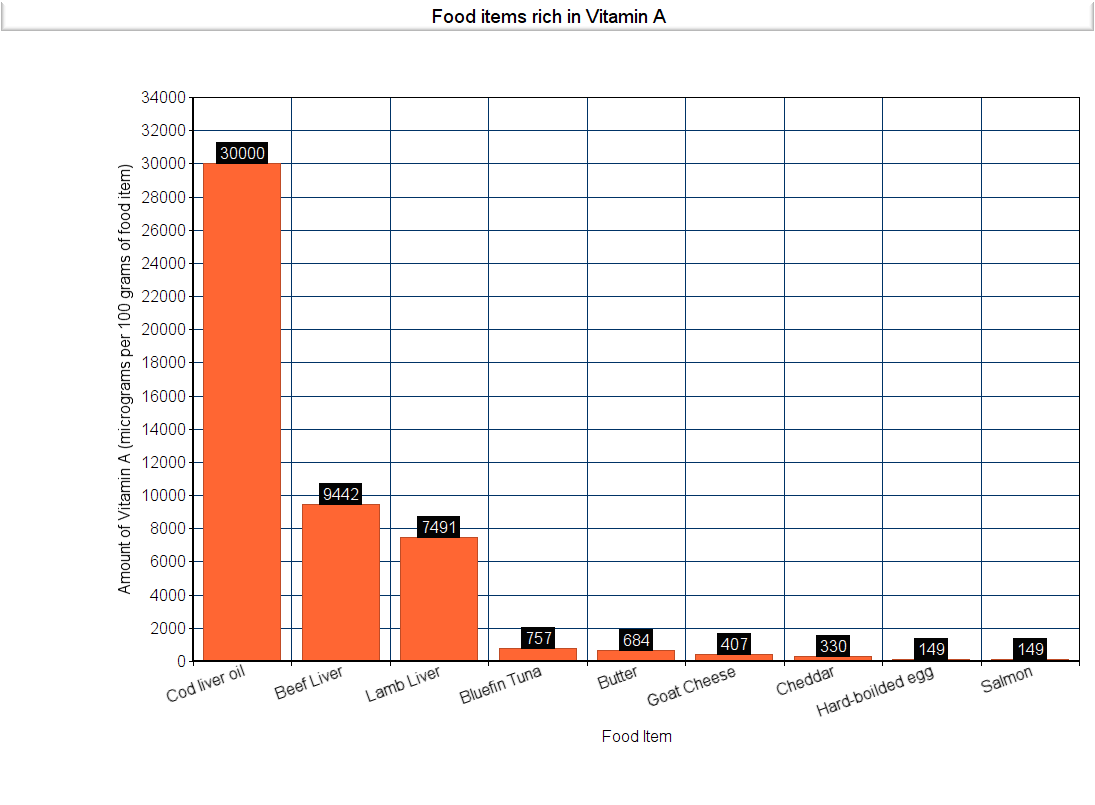
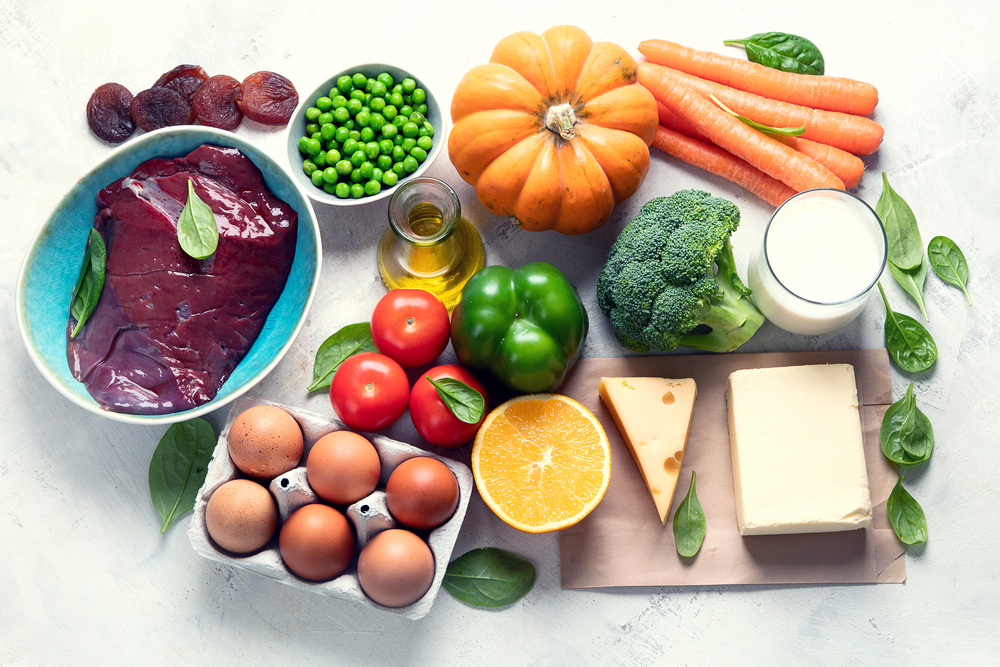
Sources
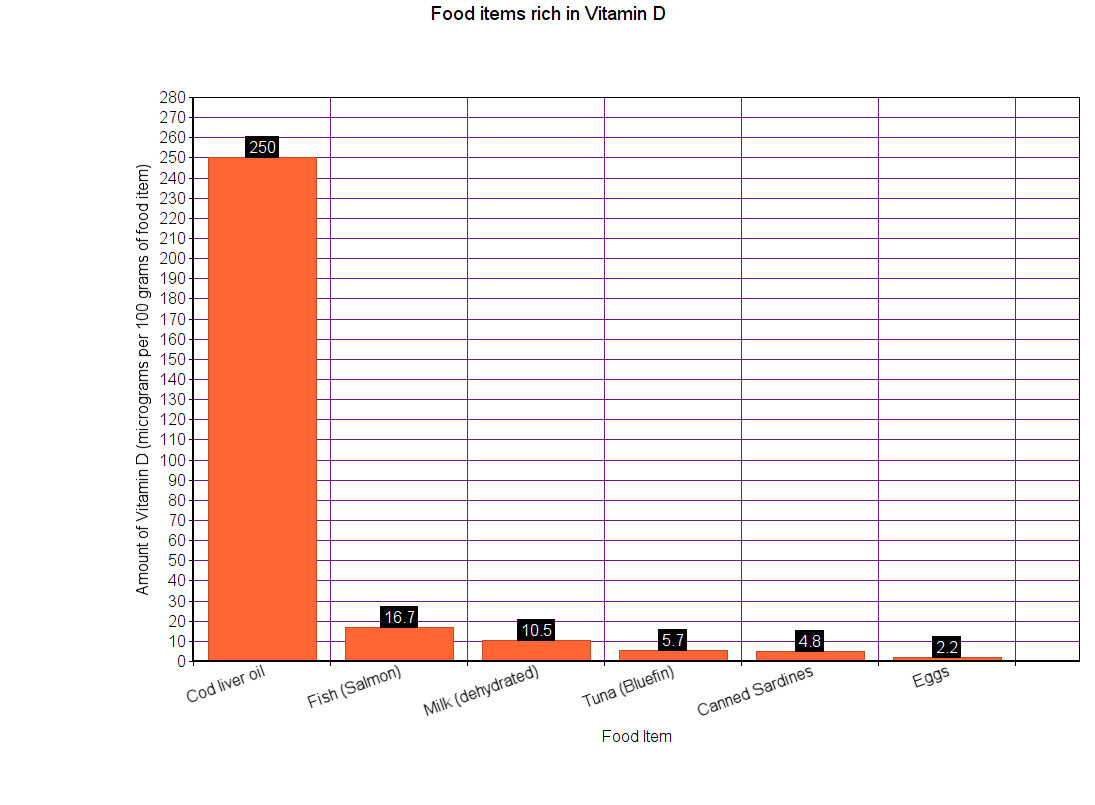
Vitamin A is only found in animal products, such as cheese, butter, cod liver oil, etc.
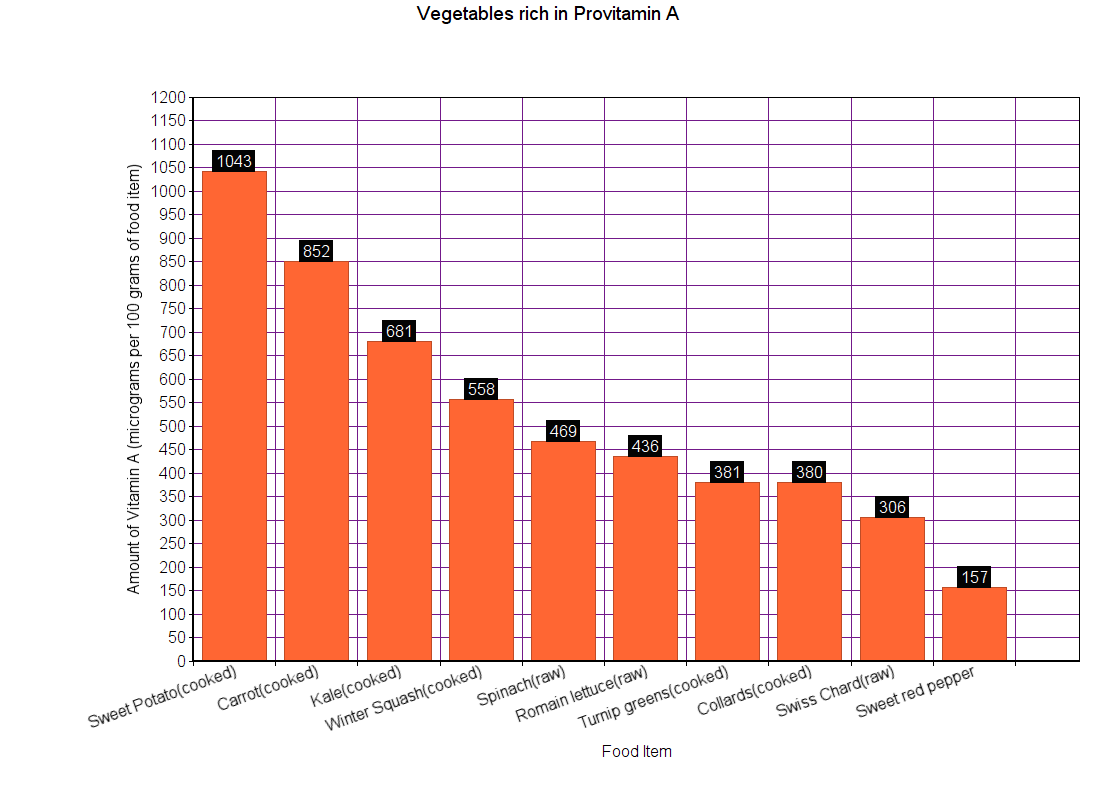
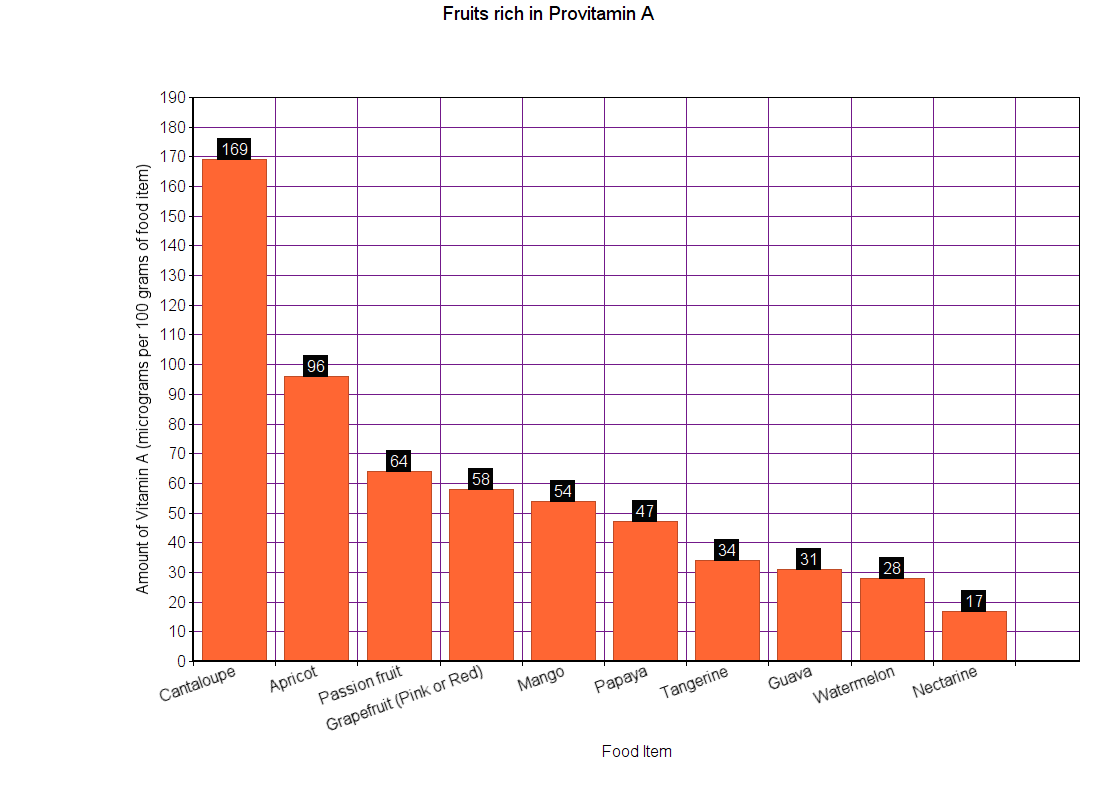
Some vegetables and fruits contain Carotenoids (alpha- and beta-Carotene). Your body can convert these Carotenoids into vitamin A. So, Carotenoids are also called as Provitamin A because they are one stage before vitamin A. These carotenoids are excellent antioxidants.
However, not everyone’s body is equally effective in converting Carotenoids into vitamin A. Roughly, 45% of the people contain a gene that decreases the conversion rate. So, if you are a vegan, or depend primarily on vegetable supplies for vitamin A, the graphs below may not hold true for you.
Since fat-soluble vitamins are easily absorbed when eaten along with fats, add a little oil to your salads.
Best practices
How to absorb Vitamin A effectively?
1. Vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin. To absorb it effectively, take some fats along with it. If you eat a diet less in fat every day, your body’s ability to absorb vitamin A will be reduced considerably.
2. Animal sources contain vitamin A in their direct form. Plant sources only contain provitamin A, which has to be converted into vitamin A by your body. So, try to consume more animal sources of vitamin A. If you are a vegan, add olive oil (fat) to your vegetables.
3. Don’t take vitamin A supplements on an empty stomach. It may lead to indigestion and heartburn. In addition to that, vitamin A may not be absorbed by your body.
4. Eating Avocado increases the absorption of vitamin A since it contains good fats.
5. Zinc is also essential for the body to absorb vitamin A effectively. Add food items like cashews, kidney beans, chickpeas, almonds, chicken, and pork, which are rich in zinc, to your diet.
6. Drink less alcohol and avoid taking weight loss medicines, to absorb vitamin A better. Ask your doctor if your existing medications affect your body’s ability to absorb vitamin A effectively.
7. Cooking can break down the thick cell walls of many plant items and release the nutrients stored in them, thereby helping your body absorb vitamin A better.
Who should take supplements?
Premature infants, breast-feeding moms, and pregnant women in developing countries are at risk of vitamin A deficiency. Hence, they might benefit from vitamin A supplements.
However, pregnant women are normally advised not to take any vitamin A supplements because too much vitamin A can cause birth defects in the baby.
So, it is advisable to consult your doctor before taking any supplements.
How much of the vitamin does your body absorb from your diet?
Your body can absorb 75% to 100% of the vitamin A you consume through food. However, it can take a long time to be absorbed.
How long does the vitamin stay in the body?
Vitamin A can stay in your body for a very long time – up to several years.
What happens to any excess of the vitamin you consume?
Any excess of the vitamin A you consume will be stored in your liver for years.
Food vs. supplements
Try to consume vitamin A through diet because vitamin A consumed through natural sources of food has a better absorption rate than the synthetic form of the vitamin consumed through supplements.
Identify this fat-soluble vitamin – 2
Calcium and Phosphorous play a vital role in the formation and maintenance of bones and teeth. The primary function of this fat-soluble vitamin is to improve the absorption of these minerals. It also strengthens the immune system.

Deficiency
As a result, the lack of this fat-soluble vitamin may cause bowed legs (Rickets) in children and loss of bone mass (Osteoporosis) and/or weak bones and weak muscles (Osteomalacia) in adults.
It can also lead to an increased risk of autoimmune diseases, cancers, infectious diseases, slow wound-healing, and hypertension.
This is one of those fat-soluble vitamins that people in countries that have snowy winters lack.
Overconsumption
Overconsumption of supplements of this vitamin can lead to increased levels of Calcium (Hypercalcemia) in the body. It can be identified by symptoms like head-ache, weight-loss, heart and kidney damage, and loss of appetite.
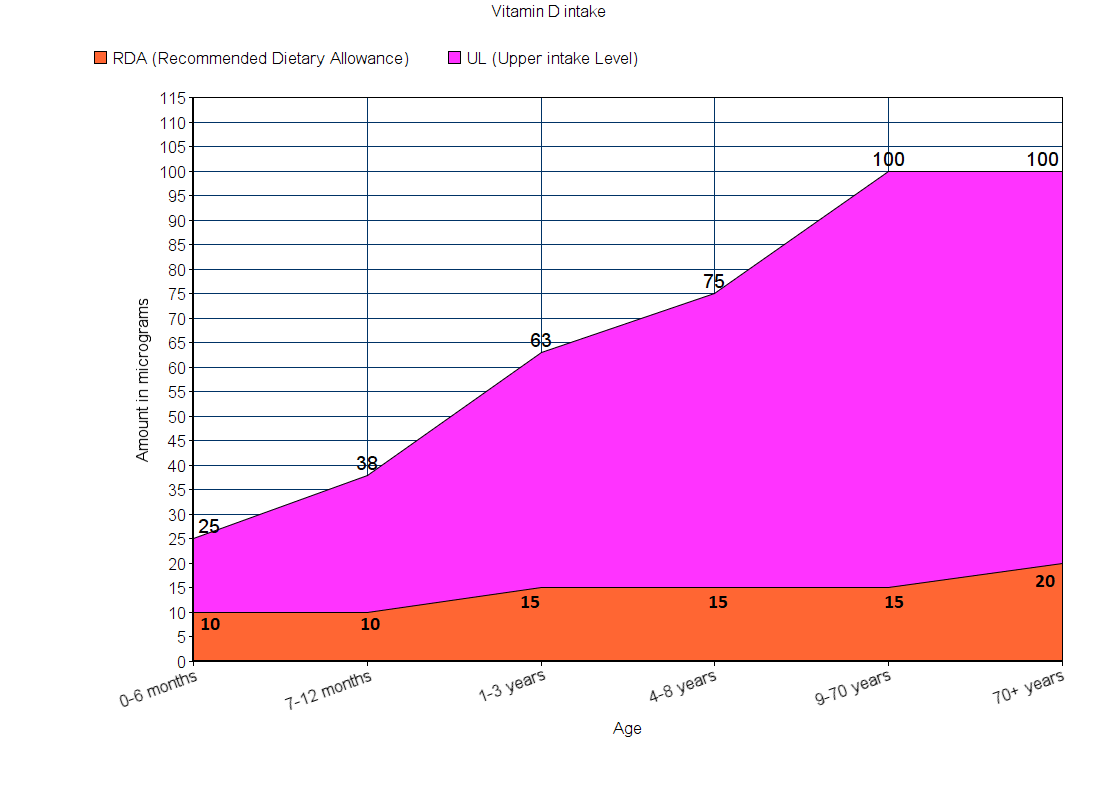
Which vitamin is it? – Vitamin D
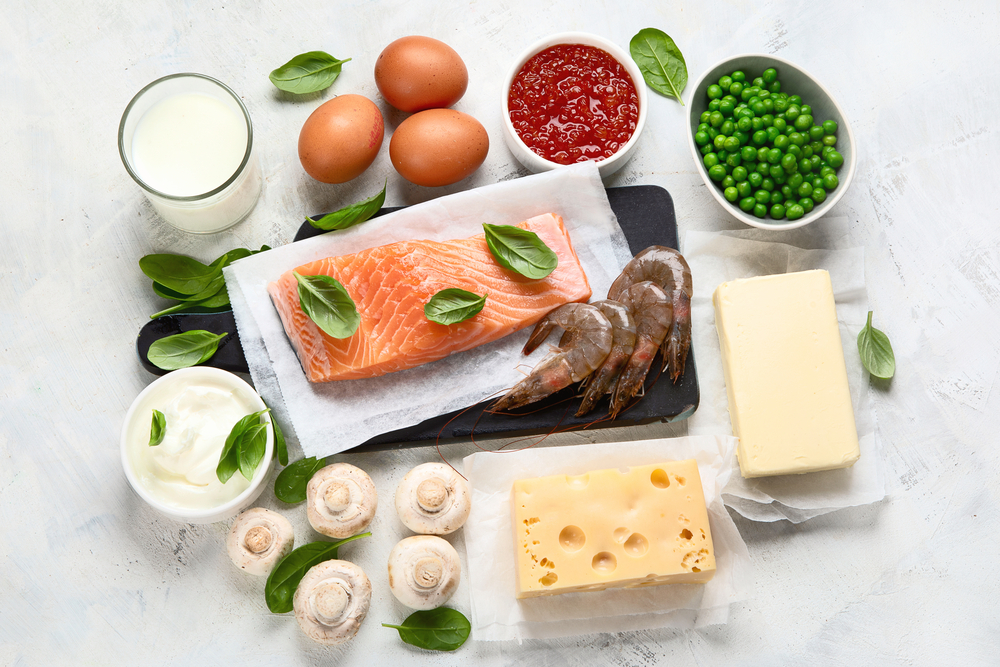
Sources
The primary source of vitamin D is sunlight. Twice a week, taking a short walk for 15 minutes, with your arms, hands, and legs exposed, without any sunscreen, is enough to get sufficient vitamin D.
The recommended daily intake of vitamin D (either as food-items or supplements) is given in the graph below.
Note: All values are in micrograms
Note: For infants less than a year old, RDA is not known accurately. Hence AI is shown instead.
Vitamin D can also be found in some animal and plant products.
Best practices
How to absorb vitamin D better?
1 Vitamin D is a fat-soluble protein. So, eat it along with foods rich in fat like avocados, eggs, seeds, and nuts.
2. Don’t take vitamin D supplements on an empty stomach.
3. Take vitamin D supplements along with a meal.
4. Research doesn’t clearly indicate if vitamin D is effectively absorbed by taking it in the morning, afternoon, or night.
Who should take vitamin D supplements?
1. People who stay indoors or apply sunscreen or cover their entire bodies whenever they go out need vitamin D supplements.
2. Human milk contains very little Vitamin D. Therefore, breast-fed infants who are not exposed to sunlight should be given vitamin D supplements.
3. In comparison to light skin, dark skin synthesizes less vitamin D when exposed to sunlight. So, people with dark skin, who spend less time in sunlight need to take vitamin D supplements.
4. The bodies of older people cannot synthesize vitamin D upon exposure to sunlight as effectively as younger people. So, older people who prefer to stay indoors are at a greater risk of vitamin D deficiency. Therefore, they should take vitamin D supplements.
5. The ability of people who are obese or have inflammatory bowel syndrome, to absorb vitamin D is highly reduced. Hence, they should take vitamin D supplements.
How long does the vitamin stay in the body?
Vitamin D can stay in your body for a maximum of two months.
What happens to any excess of the vitamin you consume?
The liver and the adipose tissues, located under the skin and around the internal organs, store excess vitamin D.
Food vs. supplements
If you live in countries where sunlight is a scarce resource, particularly in winter, you may have vitamin D deficiency. Vitamin D is difficult to get from food alone. So, eating food items rich in vitamin D, fortified foods, and/or multivitamin tablets can provide your body enough vitamin D. But make sure you don’t overdose on vitamin D.
Identify this fat-soluble vitamin – 3
This fat-soluble vitamin acts as an antioxidant and protects the red blood cells, vitamin A and C, and fatty acids in your body from destruction by free radicals.
Food for thought: What does an antioxidant do?
A free radical is an atom or molecule whose electron has been removed. As a result, a free radical is unstable and in constant search of an electron to become stable.
It can steal an electron from your DNA, cell membranes, and proteins, thereby damaging them. This process, called oxidation, can disrupt the normal functioning of the cells in your body, eventually killing them.
Free radicals are created in your body due to various substances, including fried foods, pesticides, air pollutants, smoking, and drinking.
Antioxidants donate an electron to these free radicals before it can interact with body cells. Thus, antioxidants protect the cells in your body from getting destroyed by free radicals.

Deficiency
The deficiency of this vitamin is very rare in healthy people. It can occur in people who can’t absorb fats (due to liver diseases) and also in premature infants.
Symptoms include a weak immune system, weak muscles, numbness, and difficulty in seeing and walking.
Overconsumption
Overconsumption of this vitamin can only happen due to supplements, not because of food items.
It can prevent blood coagulation and lead to excessive bleeding. In extreme cases, the process of antioxidation could get reversed.
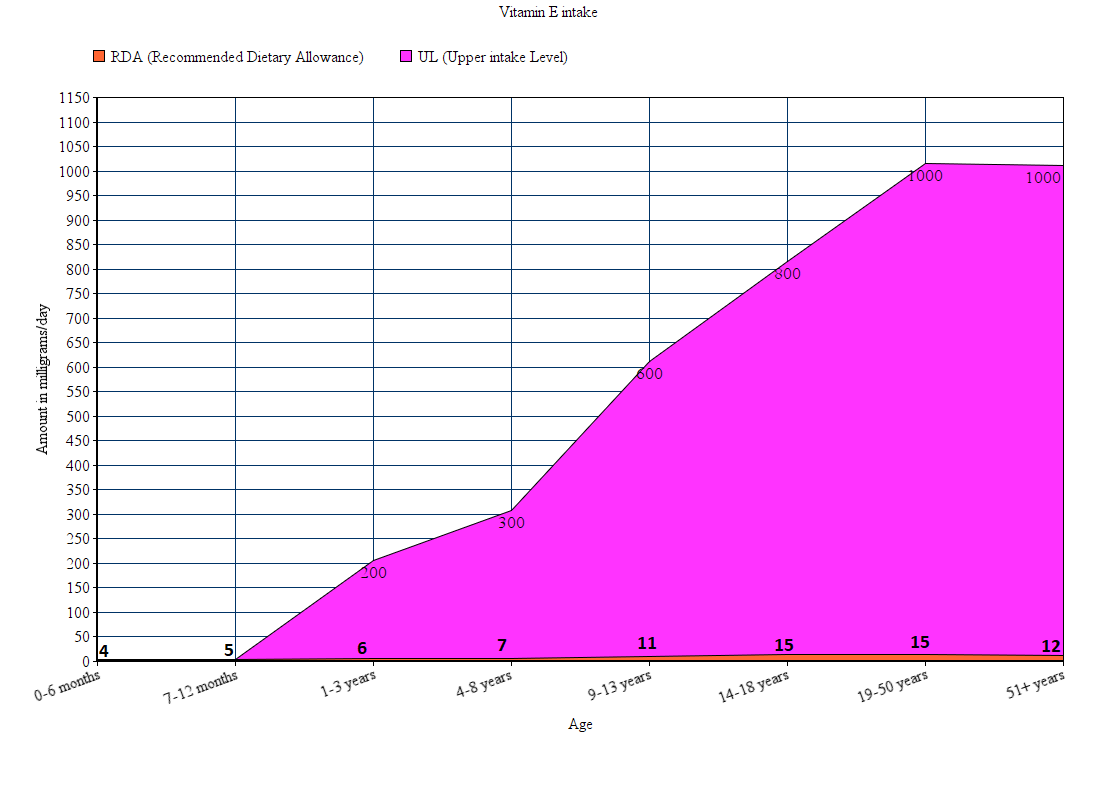
Which vitamin is it? – Vitamin E
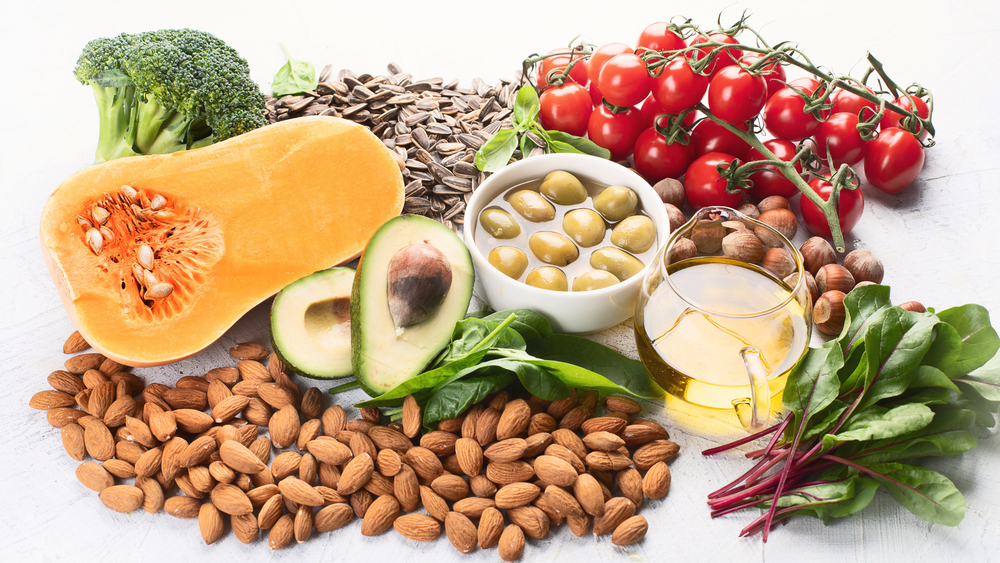
Sources
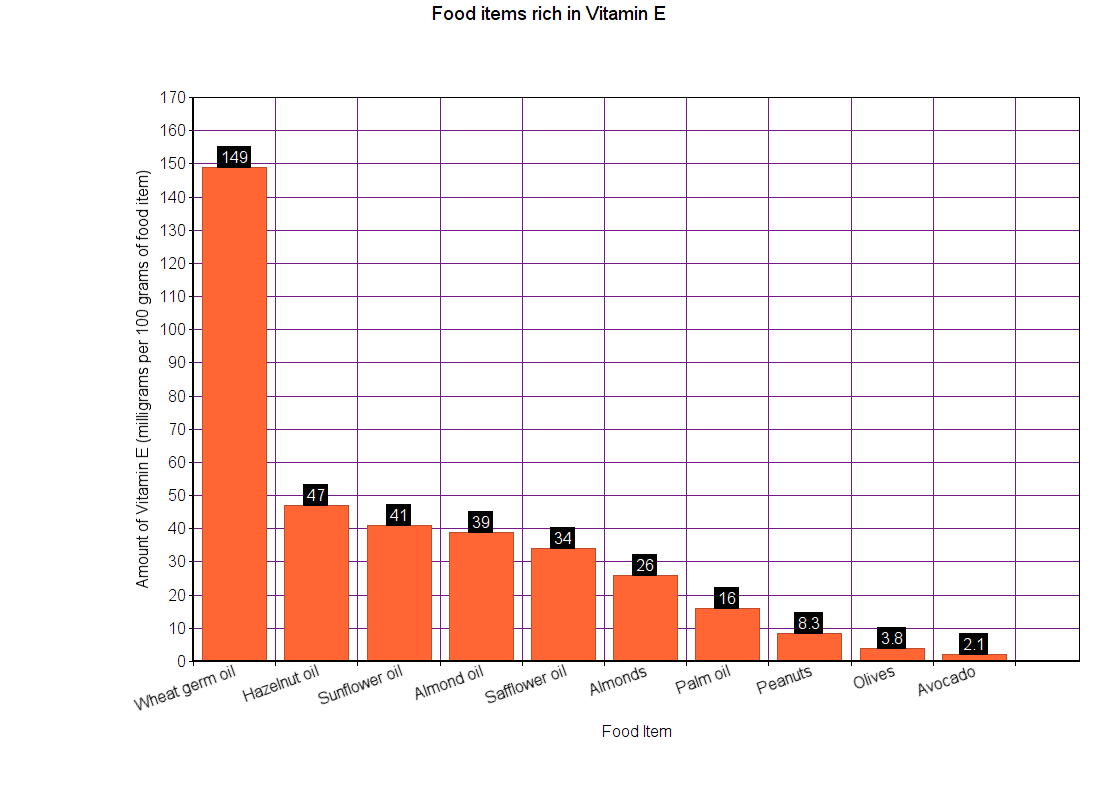
Vitamin E is primarily found in oils, nuts, and seeds.
The graph below shows the recommended intake of vitamin E for all age groups.
Note: All values are in milligrams.
Note: For infants less than a year old, UL is not known accurately, and instead of RDA, AI is shown in the graph.
The following are the sources of vitamin E.
Best practices
How to absorb vitamin E effectively?
As vitamin E deficiency is rare in healthy people, just by adding a few fats, you can absorb vitamin E easily. Adding a few almonds or sunflower seeds to your diet can improve the vitamin E intake considerably.
Who should take supplements?
There are no proven advantages in taking vitamin E supplements. The RDA of vitamin E required to maintain a healthy body can be obtained solely from natural products.
How much of the vitamin does your body absorb from your diet?
The absorption rate and the time it takes to absorb vitamin E can vary from person to person.
How long does the vitamin stay in the body?
Vitamin E can be stored in your body for several days to several months.
What happens to any excess of the vitamin you consume?
Any excess vitamin E is stored in the liver, muscles, and adipose tissues of your body. Adipose tissues are tissues located under your skin and around the internal organs of your body.
Food vs. supplements
Synthetic forms of vitamin E (from supplements) are cheaper. However, vitamin E from food is absorbed better and can be twice as effective as synthetic forms.
Identify this fat-soluble vitamin – 4
Bacteria in the intestines produce this vitamin naturally. This vitamin plays a vital role in blood clotting. It also improves bone health and reduces the risk of heart diseases.

Deficiency
Your body doesn’t store high amounts of this vitamin, unlike other fat-soluble vitamins. So, if you don’t consume sufficient amounts of this vitamin, it can lead to deficiency within a week.
Just like vitamin E, deficiency of this vitamin is rare. It occurs in people whose fat-absorption abilities are impaired due to inflammatory bowel diseases, etc.
Overconsumption of vitamin A reduces the body’s absorption of this vitamin. Overconsumption of vitamin E counteracts this vitamin’s ability to clot blood.
Lack of this vitamin prevents blood from clotting quickly. It reduces bone health, thereby increasing the risk of fractures.
Overconsumption
Overconsumption of this vitamin can kill red blood cells, change blood clotting times, and damage the liver.
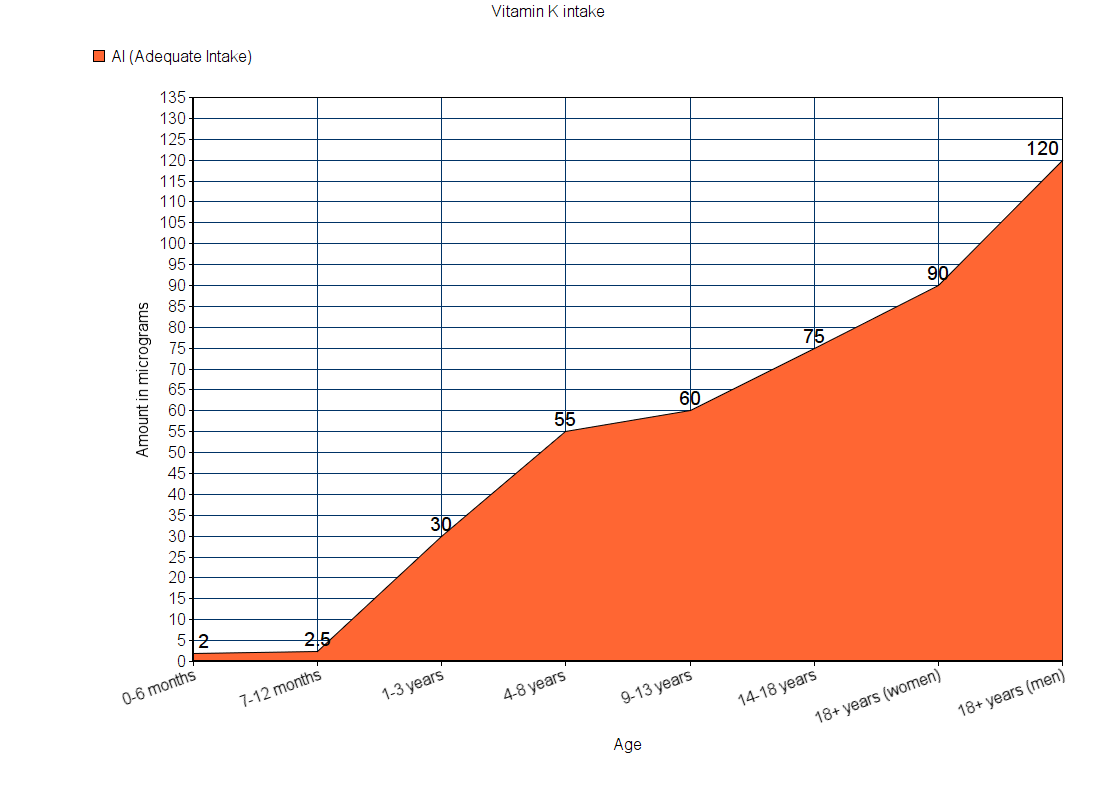
Which vitamin is it? – Vitamin K
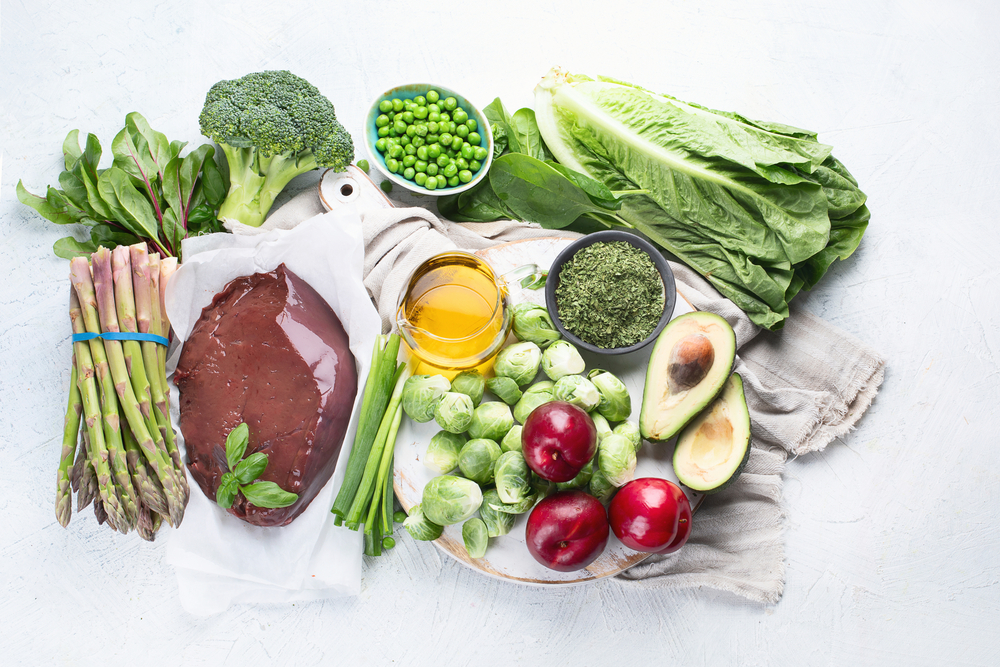
Sources
In the case of vitamin K consumption, the RDA is not known; only the AI (Adequate Intake) is known.
Note: All values are in micrograms.
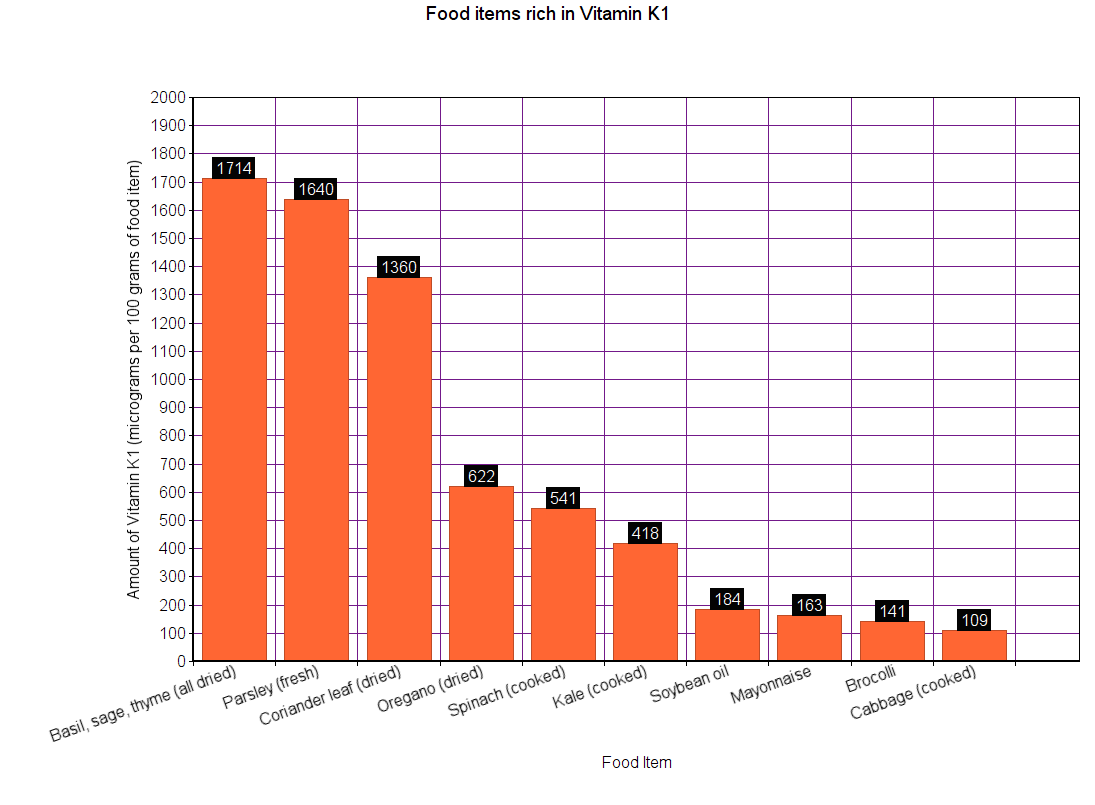
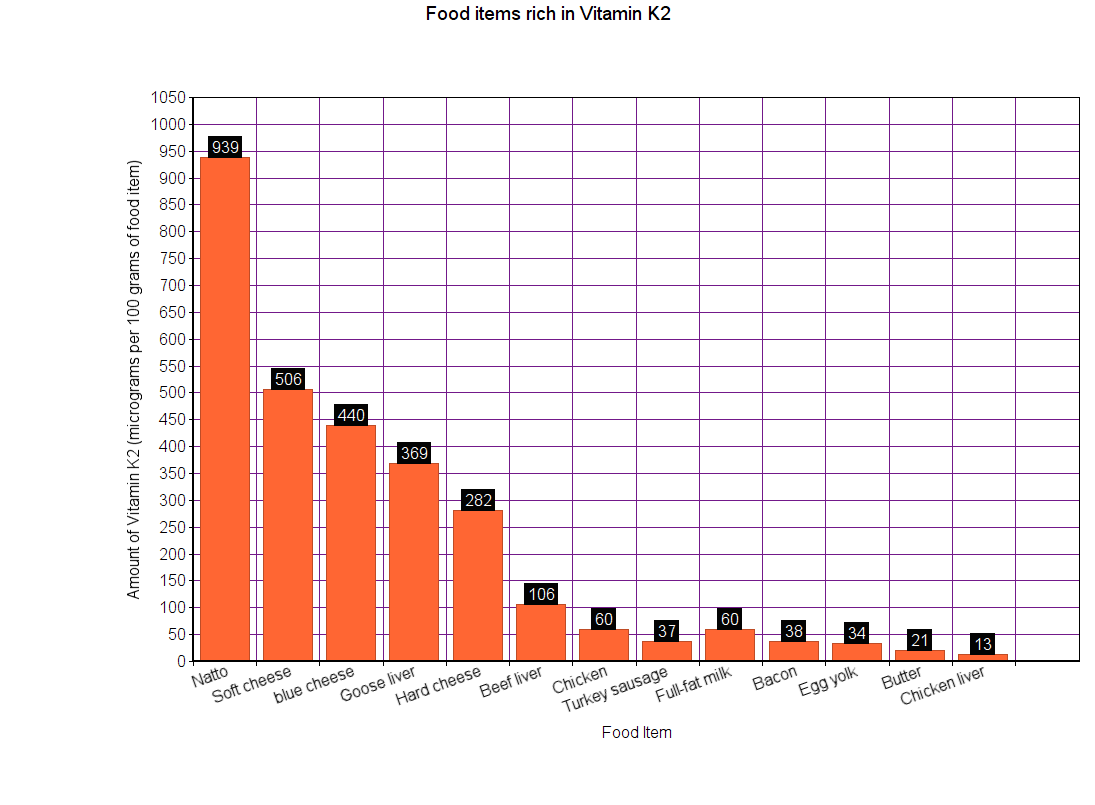
Vitamin K can be further divided into vitamin K1, K2, K3, K4, and K5. Of these, vitamins K1 and K2 play a significant role in improving your health.
K1 keeps the insulin levels balanced, reducing the risk of Diabetes. It is primarily found in plant products.
K2, on the other hand, appears to enhance the quality of bones, reducing the risk of fractures. It is primarily found in animal products. Bacteria in your gut also produce K2, but only in small amounts.
Best practices
How to absorb vitamin K effectively?
Vitamin K is a fat-soluble vitamin. So, adding fats like Olive oil, etc. to your salads can help you absorb vitamin K easily.
Who should take supplements?
Studies, done mostly in Japan, indicate that vitamin K can improve bone quality and reduce the risk of fractures. However, they were done on a small group of people — consequently, no proof between taking vitamin K supplements and its health benefits could be established.
People taking blood-thinning medicines should not take vitamin K supplements.
How long does it take for your body to absorb the vitamin completely?
It can take more than 48 hours for your body to fully absorb vitamin K.
How long does the vitamin stay in the body?
It takes 48 hours for your body to completely absorb vitamin K. The absorbed vitamin K remains in your body for a maximum of a few weeks.
What happens to any excess of the vitamin you consume?
Excess vitamin K is stored in the liver and the fatty tissues.
Food vs. supplements
Natural forms of vitamin K are safer and more effective than synthetic forms.
Summary
Vitamins A, D, E, and K are the four fat-soluble vitamins.
Eat a diverse diet containing meat, eggs, fruits, vegetables, greens, nuts, and seeds to get sufficient amounts of these four fat-soluble vitamins.
Since they are soluble in fat, add small amounts of fats like oil or butter. This will help your body absorb them easily, quickly, and efficiently.
The charts in this blog post can help you figure out know how much of these vitamins to consume and from where to get them. You can even print them out if you want to.
Usually, taking supplements for any of these vitamins is not necessary. However, if you are a vegan, you may suffer from vitamin A deficiency, and if you spend a lot of time indoors, you may suffer from vitamin D deficiency. In these scenarios, taking vitamin A or vitamin D supplements might be a good idea.