There are different types of waves in this world. Every day, they affect us in one way or the other. But before we look at these different types of waves, we have to understand what a wave is.A wave is a vibration, oscillation or disturbance traveling through a medium which transfers energy from one particle in the medium to another but doesn’t displace the medium itself permanently.
Why is the study of waves important?
Waves are important to understand a variety of physical phenomena that happen around us everyday. From water waves to seismic (earthquake) waves that can cause a lot of destruction to life and property, from radio waves that form the basis of telecommunication to microwaves that help us cook food, from UV rays that can damage our skin to X-rays that have medical applications, they are everywhere.
Understanding the concept and functioning of waves can not only help us understand how various devices work, but also help us protect ourselves from the harmful effects of certain phenomena.
Types of waves
There are three major types of waves.
1.Mechanical waves
A mechanical wave is created by an oscillation or a disturbance (caused by a source) in an elastic medium (gas, liquid or solid). This disturbance causes a movement of the particles (which also gain energy) in the medium directly in contact with the source. These particles in turn transfer their energy to the nearby particles and so on. This leads to a transfer of energy and the propagation of the wave through the medium.
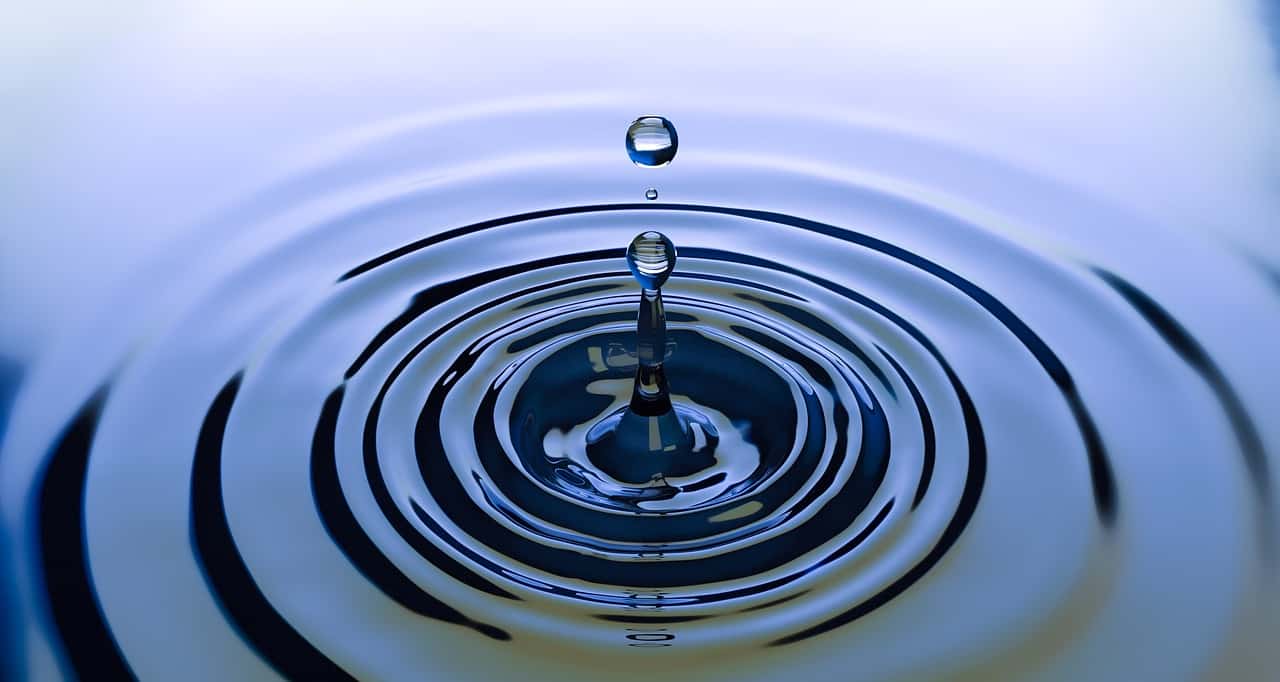
Example: A classical example is a stone falling into a pond or a lake. You can observe that ripples (waves) are created from the point where the stone falls into the water, moving outward. This is because, at the point where the stone touches the water, it displaces the water molecules that it directly comes in contact with. These water molecules gain energy, move and transfer the energy they gained to the nearby water molecules, which start moving. Then the nearby molecules do the same to the water molecules near them and so on. This movement of molecules creates a wave along the surface of the lake or pond.
To understand mechanical waves better, we should learn about the three types of mechanical waves and how they differ from each other.
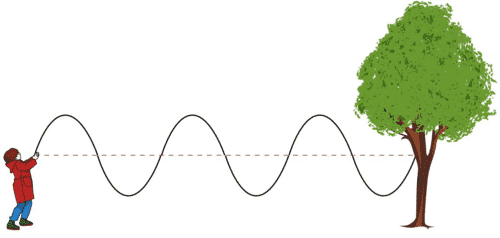
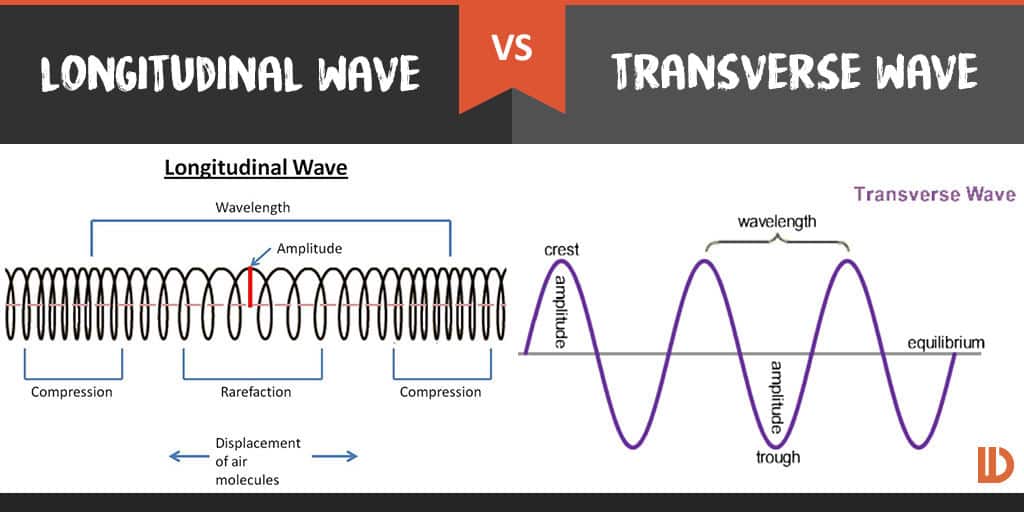
Transverse waves
When the particles in the medium move in a direction perpendicular to the direction of movement of the wave, we call such a wave a Transverse wave.
When you attach one end of a rope to an immovable object and move the other end of the rope up and down, the resulting wave is a transverse wave.
As you can see from the image below, while the wave is moving from left to right, the particles are just moving up and down. You can select a single particle to observe its motion.
Examples – Vibrations in a guitar string, electromagnetic waves
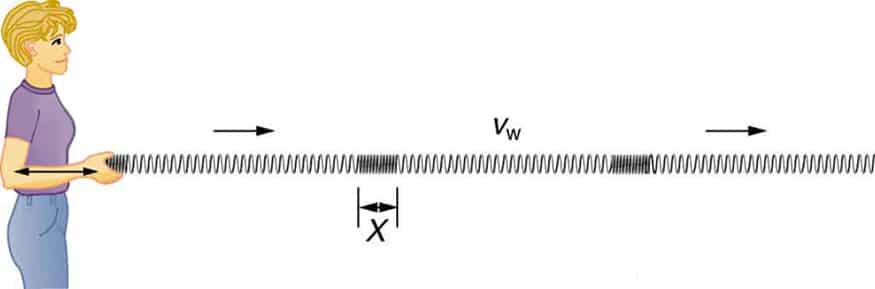
Longitudinal waves
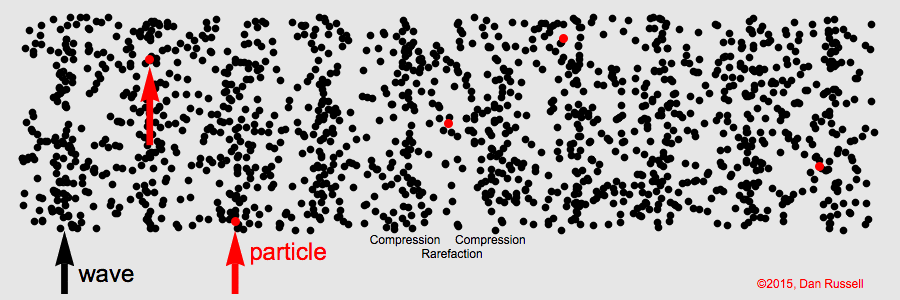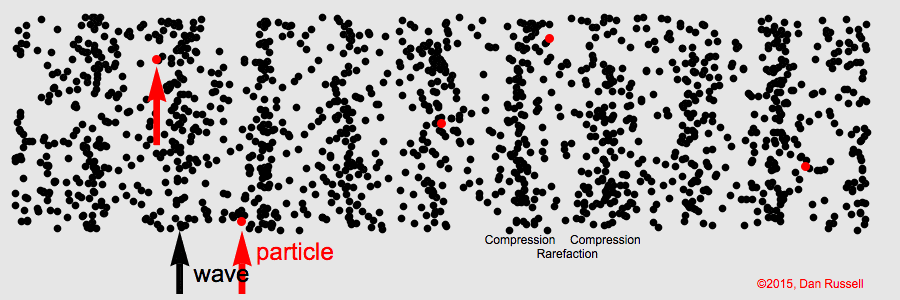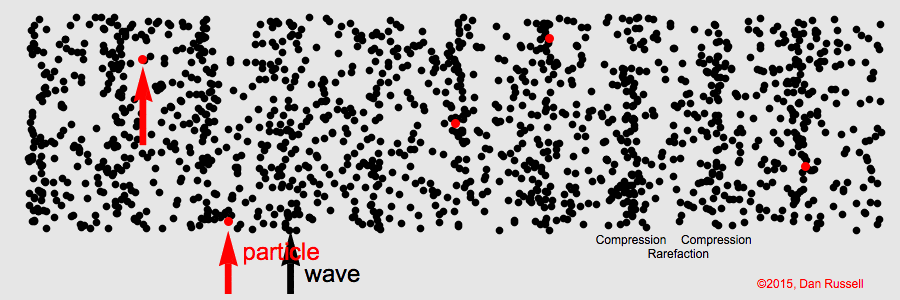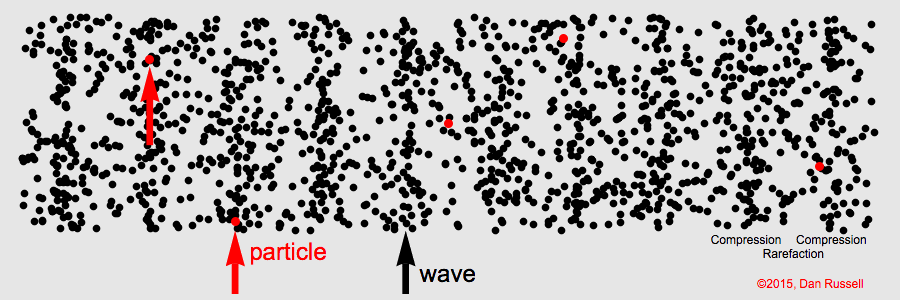
When the particles in the medium move in the same direction as the wave, the wave is called a longitudinal wave. Longitudinal waves always require a medium.
If you attach one end of a slinky or a spring to a immovable object and push and pull the other end, the resulting wave is a longitudinal wave. In the image below, as you can see, the wave moves from left to right (the Compressions form the wave) and the particles oscillate from left to right and right to left.
Example – Sound waves
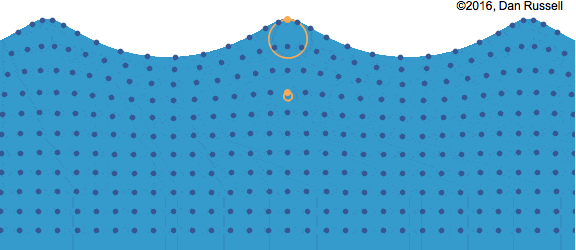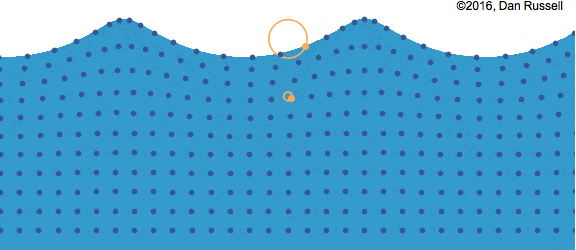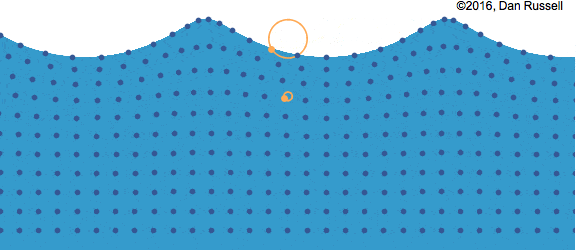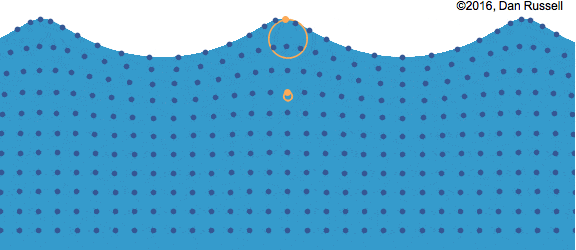
Surface Waves
Surface waves are created when a disturbance occurs at the interface between two mediums.
Waves caused by wind on the surface of water (interface between air and water, 2 different mediums) is the most common example of surface waves. A surface wave is characterized by the circular motion of the particles in the medium and can be considered as a combination of both longitudinal and transverse waves.
In the picture above, you can see that while the wave moves from left to right, the particles follow a circular path. At the top and bottom of the circle, the particle can be thought of moving left to right and right to left (longitudinal), whereas at the left and right side, it can be thought of moving from top to bottom and vice versa (transverse). This can also happen at the interface between 2 liquids like water and oil.
2. Electromagnetic waves
Produced by the vibration of charged particles, electromagnetic waves don’t need a medium for propagation. Therefore, they can travel through solid, liquid, gas and vacuum. Created by the interaction between electric and magnetic fields, electromagnetic waves can be further classified into different waves depending on the frequencies. They look like transverse waves (sine waves) and some of the properties of transverse waves apply to electromagnetic waves as well.
Example – X rays, UV rays, Infrared rays, visible light, etc.
You can read more about electromagnetic waves in our blog post here: 7 types of electromagnetic waves.
3. Matter waves
Till 1900 light was thought to be a combination of electromagnetic waves, whereas matter was thought of as a combination of localized particles. However, Albert Einstein proposed that light is made up of photons which can have both particle as well as wave nature.
In 1924, De Broglie proposed that similar to photons, electrons can also exhibit wave properties. Since then, it has been experimentally proven that electrons, neutral atoms and even molecules have wave-like properties.
Simply put, the wave produced by matter (like electrons, neutral atoms and molecules) is called matter wave.
Properties of a wave
Waves have some properties that define a wave.
Wavelength: Length between 2 consecutive maxima or minima
Frequency: Number of maxima or minima produced in one second
Amplitude: The magnitude of a maximum value or a minimum value
Crest: Maximum value in a transverse wave
Trough: Minimum value in a transverse wave
Compression: Most compressed part in a longitudinal wave
Rarefaction: Least compressed part in a longitudinal wave
Facts you probably didn’t know
- Both longitudinal and transverse waves can move through a solid. However, only longitudinal waves can travel through liquids and gases. That is how we know that the core of the earth is made of liquid (mostly molten iron). Earthquakes produce seismic waves that are both longitudinal and transverse waves. However, from the other side of the earth, a major part of the transverse waves couldn’t be detected, but most of the longitudinal waves were detected. Since transverse waves cannot move through liquids, it was deducted that the core of the earth is molten.
- If it were not for electromagnetic waves, we would not have been alive now. Light waves, which are electromagnetic waves that don’t need a medium for propagation, from Sun made photosynthesis possible thereby creating complex life on earth.
- The waves produced by throwing a stone into water and by blowing wind across its surface are not the same. While wind produces only surface waves along the surface, a stone thrown into water also produces (in addition to surface waves) longitudinal waves in its direction of movement, while moving to the bottom of the water body.
- Electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light.
- Light travels faster than sound. That is why we see the lighting before we hear the thunder.
- You cannot hear sounds in space because, there is no medium in space for the sound (longitudinal waves) to travel.
Did this blog post help you learn about the different types of waves?
Did this blog post help you learn about the different types of waves? Then share it with your friends today.