GPS:
GPS stands for Global Positioning System. It is a radio-navigation system consisting of 31 NAVSTAR GPS satellites orbiting at a height of 20,000 km from earth. If you remember what we learned about Satellites, you might know that GPS satellites orbit the earth in the medium-earth orbit with a semi-synchronous orbit.
These satellites are owned by USA and operated by the US Air Force. It is the process of finding a device’s (with a receiver) position on or near the surface of the earth with
an accuracy of 30 cm (as of 2018). Satellites transmit radio signals (microwaves) at a frequency of 1575.42 MHz.
What are the three components of a GPS system?
The GPS system consists of a transmitter (GPS Satellite) that transmits the radio aves, a receiver (your phone) that receives the radio waves and evaluates the signals and a medium (air) through which it travels. Note that, since GPS uses microwaves (a type of
electromagnetic waves), it doesn’t require a medium (gas, liquid or gas) for communication.
How does GPS work?
GPS works on the principle of trilateration. Watch this video from NASA that explains the concept of GPS and trilateration.
If you don’t want to watch the video, the same concept is explained below:
The concept is difficult to explain in 3D. So, let’s explore this in 2D. Take a look at the picture below.
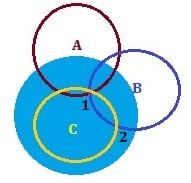
Trilateration
Think of the Blue circle as the earth. Let’s say that you are standing on it at the point ‘1’. You have a cell phone with GPS (receiver) enabled and you want to find your position (to navigate to an address using Google Maps). Now, the Cell phone communicates with the satellite C, which returns the distance of the receiver from its location. Let’s draw a circle with that distance as radius and satellite C as center. Your phone (and you) can be anywhere on this Brown circle. It’s not enough to find your location though.
So, the receiver communicates with the next satellite (satellite B) and gets its distance from that satellite. So, now your phone knows its distance from these 2 satellites (B and C). It can be only in one of the 2 intersecting points ‘1’ or ‘2’, because the two circles, drawn using the distance of your phone from these satellites and these satellites as centers, meet only at these two points.
Now by knowing the distance of your phone from the third satellite, you can pinpoint the location of your phone to point ‘1’.
This concept is called Trilateration. By knowing the distance of a receiver from 3 satellites, its location in 2D can be calculated. Similarly, to find its location in 3D, 4 satellites are required. By having 24 GPS satellites, every location in earth can be tracked by 4 satellites at any given time. There are more than 5 spare satellites as well.
How does your phone differentiate between the signals from different satellites?
Each GPS satellite broadcasts a navigation message continuously at 50 bits/s. Broadcasting is a process in which a transmitter sends a message without a recipient address. All the receivers who are listening can receive this message. This navigation message consists of the following details and is 1500 bits long.
1. Time of week
2. Week number
3. Health report of the satellite (to find out if the satellite is malfunctioning)
This message is then encoded in a PRN code. All the GPS receivers know the PRN codes (sequence of zeroes and ones) of all the satellites. So, from the navigation message they receive, they can easily identify the satellite.
Facts you probably didn’t know:
- A GPS signal doesn’t need an internet reception or telephonic reception.
- GPS was invented due to the need for a global navigation system during the cold war and was used only for military purposes.
- Soviet Union shot down a Korean passenger flight when it entered the Soviet airspace. This made the then American president to open the GPS for public use.
- There are GPS shoes available, which is helpful in locating people with Alzheimer’s disease.
- GPS can also be used to track time, since all the GPS satellites are equipped with atomic clocks.
- If you are traveling at a height of 18,000 m faster than 1,900 km/h, your GPS device will deactivate itself so that it cannot be used as an intercontinental ballistic missile.
- Even though US provides GPS services free of cost, US tax payers pay $3.9 million a day to keep it running.
- Most people who have cars with GPS still use their phones for direction. – Source
- If you use GPS a lot, beware. It reduces the ability of your brain to make mental maps as well as process spatial data. – Source
We hope that this blog post helped answer your question - "How does a GPS work?" If you liked this blog post, try our other science-related blog posts: