As you may already know, currencies are monitored and controlled by a central institution (the government). A country's government can control the currency's exchange rate, the amount of currency available in circulation, etc.
By determining the interest rates, governments and banks control the flow of money as well. In addition to that, banks and other financial institutions charge high transaction fees. Thus, in reality, people aren't in control of their money, even though they work hard to earn it.
The cryptocurrency was invented during the global recession of 2008 to help people take control of their money by putting an end to the traditional monetary system.
A cryptocurrency is a decentralized digital currency, that eliminates the need for a middle man. It is a currency that does not exist physically, but only digitally. Since it is decentralized (distributed), no single authority can control it.
But since no single credible authority controls or monitors it, anybody can manipulate it. Traditional currencies are tracked, monitored, and controlled by governments and banks. If not for banks, you could add additional zeros to your bank account, or lie that your company hasn't deposited your salary. But you cannot do this because banks keep track of your money and all your transactions.
But, in case of a decentralized digital currency, nobody monitors it, or tracks the transactions. So, anyone, say Mr.A, can claim that he had transferred 100 units of cryptocurrency to Mr.B. He can create a false transaction to prove this. In the worst-case scenario, Mr.B must pay the 100 units of cryptocurrency to Mr.A.
Thus, the lack of an authority to monitor transactions and detect frauds is one of the most significant problems of digital currencies. However, the first successful cryptocurrency, Bitcoin, solved this problem using Blockchain technology.

Blockchain
To understand what Blockchain is, let's consider a simple example. Let's imagine that you are a student in an examination hall. Your teacher distributes question papers to everyone, including you. Let's assume everyone gets the same question paper.
If you don't know the answer to a question, you cannot replace it with a question that you know the answer to. If you do so, your teacher can easily find out that you have tampered with the question paper. Since the question papers are copies of each other, all he/she needs to do is compare your question paper with that of another student.
Blockchain uses a similar technique for fraud detection. Blockchain is a technology that maintains a record of financial events (transactions, contracts, etc.) across several computers in a network. The transactions are stored in Blocks.
Blocks are linked to each other to form a Blockchain. As new transactions happen, more blocks are added to the existing Blockchain. A copy of the Blockchain is sent to everyone in the network whenever a Blockchain is updated. Since copies of the Blockchain exist in several computers, other computers will notice if someone tampers with a transaction in any block in the Blockchain.
Private and public keys
When you create a Blockchain wallet (similar to your bank account), you receive a public key and a private key. The private key gives you access to your account (to spend money), whereas the public key confirms the ownership of your account. The private key is kept secret, whereas the public key is shared with others.
When you initiate a transaction, three things are shared with the entire bitcoin network.
- Your message (transaction).
- Your digital signature, which is created by passing your message through a Hashing algorithm and then signing it using your private key.
- Your public key.
If you go to a bank and deposit a check, the bank employee first makes sure that the account details are correct. Then he/she checks the authenticity of the check by verifying the signature. Finally, if everything matches and the said account has the required amount of money, you get the money.
In this bitcoin scenario as well, there are people who perform the job of the bank employees. They are called Miners.
Hashing algorithm
The Hashing algorithm plays a very important role in the Blockchain mechanism. It makes sure that nobody can hack your account using the message you send.
To understand what a hashing algorithm does, let's consider an example. Assume you want to encode the text, "The Moon is black," and send it to your friend. Let's use numbers for each letter of the alphabet (a=01, b=02, z=26, and ' '='/').
So, the message will be encoded as:
The Moon is black = 200805/13151514/0919/0212010311
You can now write it on a piece of paper and send it to your friend. If he knows the encoding algorithm, he can reconstruct the original message easily. However, others won't be able to decode the message because they don't know how you encoded it.
The Hashing algorithm serves a similar purpose in the Blockchain mechanism. However, unlike our algorithm above, it is much more complex, with the following properties:
- Regardless of the input's length, its output always has the same length (256 bits = 64 hexadecimal digits).
- Its input cannot be reconstructed using its output.
- The same input will generate the same output, but no two inputs will generate the same output.
As you can see in point 2, it's impossible to obtain the input from the output (hash). So, the only way to break the algorithm or get the input from the output is by Brute-Force, i.e., hash different inputs until you find the input that created that output. Since the number of bits in the hash is 256, this would take 2^128 tries on an average. A supercomputer that tries 15 trillion entries per second would take 47,956 trillion years to find the input.
If you're interested, you can try to hash different texts using the hash calculator here.
Miners
We saw that Miners are similar to bank employees. The bank employee is hired and paid by the bank to do the job. Bitcoin miners, on the other hand, are not hired by anyone. They are users who volunteer for the job of verifying the messages (transactions) and get a reward for it. When a miner wants to verify the transactions, he selects a list of unchecked transactions. Then he starts verifying the transactions one after the other.

How does a miner check a transaction?
Whenever you make a transaction, your transaction details, digital signature, and public key are automatically shared with the entire bitcoin network.
Any Miner can take these details to check your transaction to ensure that you are the one who initiated the transaction. To do this, the message you sent is processed by a hashing algorithm. At the same time, your digital signature and public key are processed through a verification algorithm.
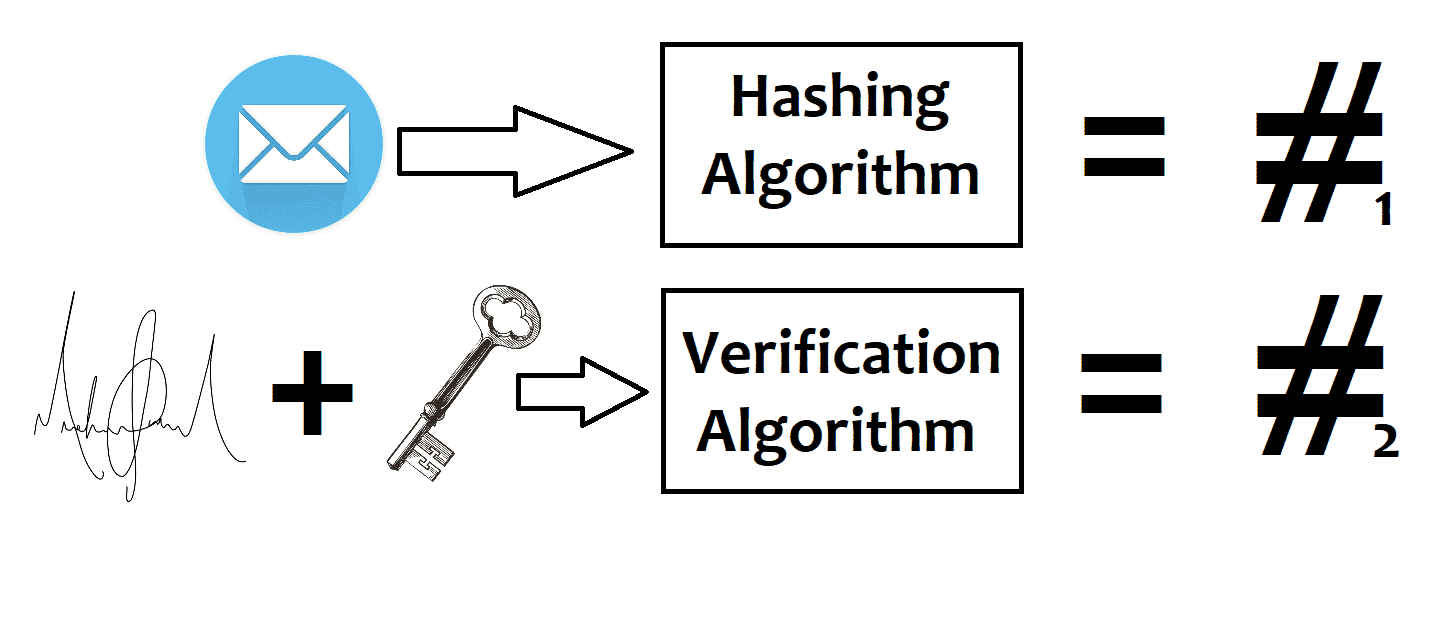
The hashes resulting from both these processes are compared. If they are the same, the message you sent and the message received by the miner are the same. If not, it indicates that someone has tampered with your message, and the miner rejects the transaction.
Then, the miner verifies that you have sufficient bitcoins to make the transaction. In the same way, he verifies as many transactions that can fit into a block.
But you should remember that the transactions are sent to the entire bitcoin network. Hence, several miners can start verifying these transactions simultaneously.
Even though many miners compete for the job, only one of them can be paid. But, since many miners may finish checking the transactions simultaneously, rewarding only one of them is difficult. So, they are assigned a very difficult puzzle to solve. The first one, to solve the puzzle in addition to checking the transactions, gets paid.
The puzzle
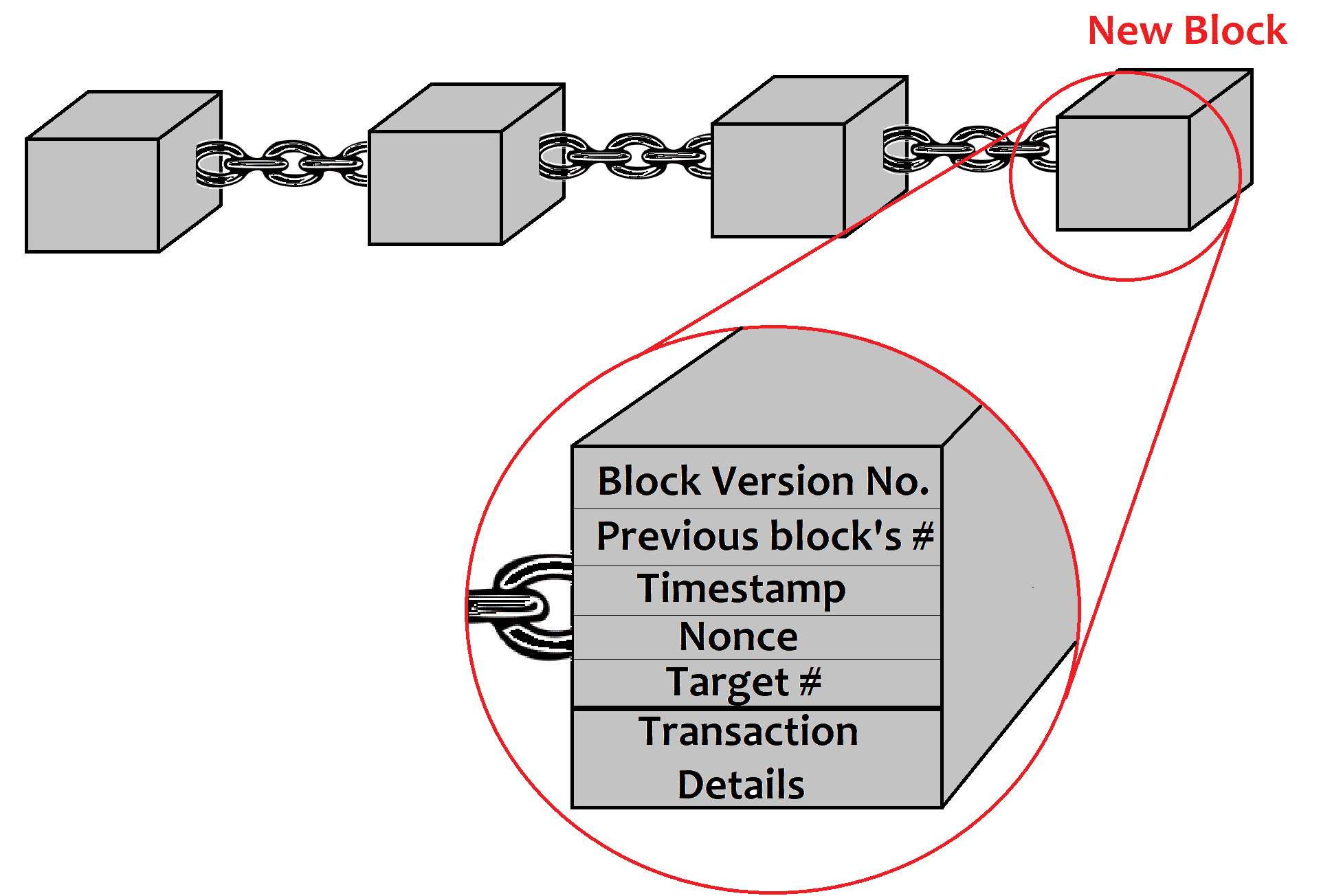
Each block is provided a target hash value (64 hexadecimal numbers). The Blocks contents, including the checked transactions and the hash value from the previous block, are hashed along with a random number (Nonce) to get a hash value. To solve the puzzle, the miner has to find a Nonce (between 0 and 2^31), so that the resulting hash value is less than or equal to the target hash value.

The reward
When a miner finds such a nonce, several things happen:
- A new block is added, and the Blockchain is updated.
- The verified transactions are removed from the available pool of transactions to verify.
- The miner gets a reward for his work.
In 2016, the reward for a miner was 12.5 bitcoins. In addition to that, the miner also collects the transaction fees for the transactions he verified. Besides being a rewarding experience for miners, mining is the only way in which new bitcoins are introduced into the bitcoin network.
The reward for mining is halved every four years. In 2020, it is expected to become 6.25 bitcoins. The maximum number of bitcoins that can be created is 21 million. In 2040, the number of bitcoins will equal this amount, and the miners will get no bitcoins for mining, but only the transaction fees for verification.
Fraud detection
As you can see above, every block's hash value changes depending on the hash value of the previous block as well as the transactions in that block. So, if someone changes a transaction in a block, the hash value of that block changes. Consequently, the hash values of all the subsequent blocks in the Blockchain change too. So, any attempts of fraudulence can be uncovered by comparing it with the blockchains stored in the network.
You can test this by changing the values in any peer in this link. The color of the corresponding block and all the subsequent blocks in that peer changes to red, whereas the Blockchain in other peers remain green. Each peer simulates a Blockchain user in the network.
Should you get into bitcoin mining?
The reward for bitcoin mining can be tempting (1 Bitcoin = $9,342 at the time of writing this article). However, the resources, processing power and electricity, needed for mining bitcoins successfully are costly. When bitcoin was introduced in 2009, the complexity of mining was very less, and the reward was high (50 bitcoins).
However, the rewards are halved every four years. Moreover, the complexity of the mining algorithm is adjusted depending on the number of miners. So, the complexity of mining increases with the increasing number of miners, which leads to increased processing power (and costs).
If you are entering the mining business now, you stand no chance against mining pools. A Mining pool is a large number of miners working together. If one of them mines a bitcoin, the profit is split among everyone.
So, bitcoin mining can actually be a non-profitable business.
Other cryptocurrencies - Ethereum
There are several other cryptocurrencies out there. But the one that has the most market capital after Bitcoin is Ethereum, which was invented in 2015.

While the concept of Blockchain and mining are similar to Bitcoin, the use and the currency of Ethereum differ. Bitcoin's use is to serve as a decentralized digital currency to monitor financial transactions. Ethereum, in contrast, serves as a digital currency to monitor smart contracts.
The digital currency of Ethereum is Ether. Unlike Bitcoin, however, there is no limit to the amount of Ether that can be mined. 18 million Ether are mined every year. This may lead to inflation, reducing the value of Ether eventually, when the supply of Ether overtakes its demand. However, due to the increase in demand as well as the complexity of mining over time, inflation may be slowed or even halted.
Smart contracts
In Bitcoin, a transaction in a block may look like:
Tom sends 100 BTC to Harry.
In Ethereum, a smart contract in a block may look like:
Send 100 ETH from Tom to Harry if Tom's balance is more than 150 ETH and the date is 11.06.2020.
Smart contracts are digital contracts and can be programmed in a special language called Solidity. Unlike Bitcoin, which requires manual transactions, in Ethereum, smart contracts can automatically trigger transactions. Smart contracts are Dapps or Decentralized applications. Smart contracts can be used for a variety of purposes, not just financial transactions.
What should you know before you get into cryptocurrency trading?
Cryptocurrency trading is similar to forex trading in some ways. So, many pieces of advice that apply to forex trading apply to cryptocurrency trading as well.
Cryptocurrencies are volatile
The prices of cryptocurrencies can vary greatly within a day. So, investing in cryptocurrency trading can be risky if you are new to it.
Leverage
Just like in forex trading, the concept of leverage exists in cryptocurrency trading as well. It can lead to quick profits as well as quick losses.
What moves the prices
Several forces including supply & demand, integration into eCommerce, security breaches, press coverage, etc. can affect the price of cryptocurrencies easily.
Uncertain future
Despite cryptocurrencies being a marvel of this century, their future is uncertain. Just like the digital currencies before them, they may go extent in the future.
Compare fees
Always compare the fees of different cryptocurrency brokers, before you choose one for trading.
Pips
A Pip in cryptocurrency trading means the same as the pip in forex trading. However, the value of 1 Pip varies from one cryptocurrency to another.
