The first world war was devastating. Even though a hundred years have passed, the aftermath of world war 1 can still be felt. Not only did it claim the lives of millions of people, but it also changed the world in many ways.
The first world war killed around 20 million people and left another 21 million wounded.
Due to the naval blockade of food and materials to Germany and its allies during the World war, an estimated 424,000 German civilians died of starvation.
How did the first world war affect the world?
If anything, the people wanted to avoid another such war. Hence, the need for an international organization to oversee global security became obvious.
The League of Nations was formed with this goal in mind. It was the first international organization that was created to maintain global peace.
The League of Nations intended to maintain peace using collective security and disarmament.
The idea behind collective security is to utilize the armies of the member nations to fight a common enemy. If a country becomes a threat to global peace, other countries send soldiers to fight this common enemy.
Disarmament is the process of utilizing agreements and treaties to limit the production and storage of weapons.
How did the first world war affect countries?
Most countries and their citizens had hoped that the first world war would end quickly. But against everyone’s hopes, the war went on for four long years. The first world war started as a war to see who was stronger. However, as the war progressed, it became a test of endurance to see who would last longer.
To survive the war, the countries invested most of their resources in the war and spared little for their citizens. As a result, civilians had little food to feed themselves and little money to spend. Therefore, as the war dragged on, people started revolting against their governments.
As a result, when the war ended, several great empires – German, Russian, Ottoman, and Austria-Hungary, fell. New countries gained independence from these former powerful empires. Due to the aftermath of world war 1, the political map of Europe changed permanently.
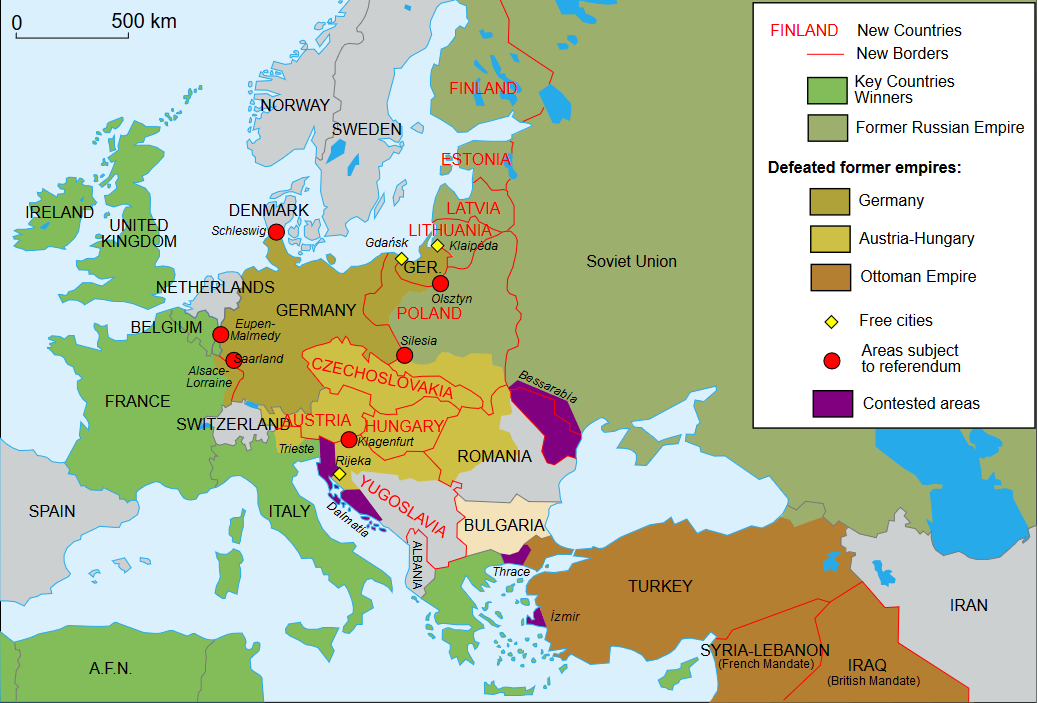
By derivative work: Fluteflute (talk)Map_Europe_1923-fr.svg: Historicair – Map_Europe_1923-fr.svg, CC BY-SA 2.5, Link
How did the first world war affect the economy?
Countries on both sides invested heavily in the first world war. Thanks to that, countries had limited resources (people and money) to invest in production, and people had less money to buy.
Consequently, the GDP of many countries declined steeply. It pushed many countries into severe debt.
Germany and Austria-Hungary, which had lost the war, had used up a majority of their resources. In addition to that, they were forced to pay war reparation costs to the winners as well.
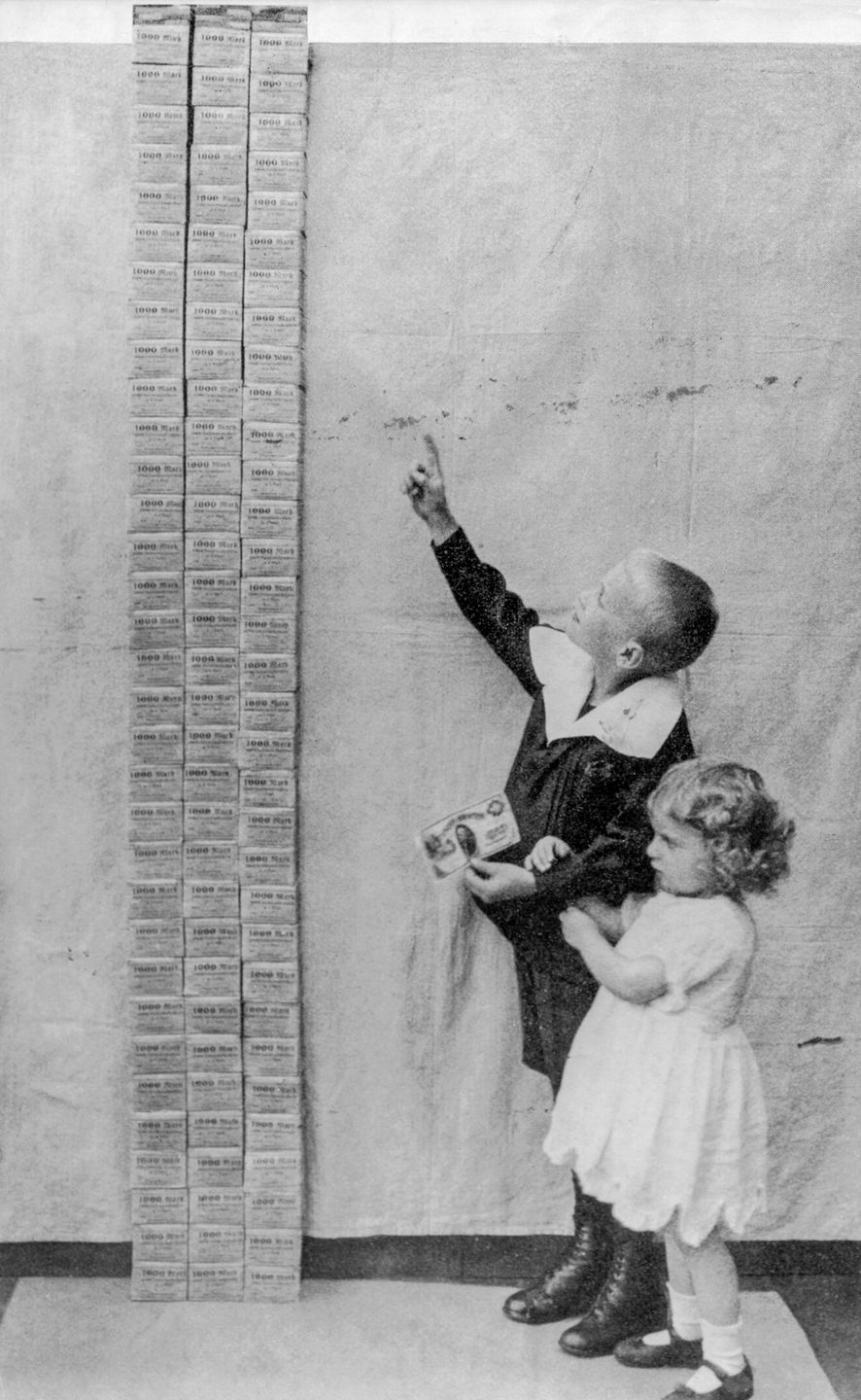
Hence, Germany’s debt rose to twenty times that of pre-war levels. Germany printed 132 billion marks to pay for the reparation costs as well. However, the production of goods did not increase. Since there was excess cash, but fewer goods for people to purchase, Germany suffered due to hyperinflation.
At a point in time, the prices of everyday items in Germany doubled every 3.7 days. For example, if you were a German at that time, if you purchased a loaf of bread for $1; the next week, you had to pay $4 for the same loaf of bread; the week after that, you had to pay $16.
When the war ended, not just the losers, but also the winners became poorer.
Britain and France, who had won the war, had borrowed heavily from the USA and had to pay it back. In fact, the last installment of the money Britain loaned from the USA was paid back only in 2015. The country also saw a rise in inflation. In 1919, people could buy only one-third of what they had purchased in 1914 with the same amount of money.
As you can see, the aftermath of world war 1 on the economies of several European countries was overwhelming. Most countries became poorer.
However, the USA, which sold weapons and oil to both sides, became richer and established itself as a superpower. Thus, the first world war broke the economic balance of the world.
Tax rates
The tax rates also increased because of the first world war. For example, the maximum tax rate in the USA rose from 15% in 1916 to 77% in 1918. Meanwhile, the standard income tax rate in the UK rose from 6% in 1914 to 30% in 1918. Germany, on the other hand, did not levy direct income taxes on its citizens. It relied on other methods to generate revenue, like floating short-term bills and issuing long-term war loans to the public.
How did the first world war affect colonies?
After the war, colonies of Germany and the Ottoman Empire were distributed among the victors of the war.
Britain experienced revolts in some of its colonies, particularly India. India sent 1.5 million soldiers, 170,000 animals, 3.7 million tonnes of food, and a large loan equivalent to 2 billion pounds today. In exchange, Britain promised to give independence to India once the war ended. However, Britain failed to keep its promise, and this led to nationwide protests against the British in India.
How did the first world war affect people?
The first world war did not just kill and cripple men. It also changed the lives of women permanently.
Women couldn’t find men to marry
Since a lot of men died in the war, the gender ratios in several countries were severely affected. For example, Germany, Austria-Hungary, and France lost 15%, 17%, and 10.5% of their active male populations, respectively.
The number of marriageable men fell significantly. As a result, women had difficulties in choosing a partner, and many of them remained unmarried.
For example, in France, of the 8.4 million men sent to war, 1.35 million men died, and 4.26 million men returned wounded. After the war, in France, for every ten women of marriageable age, there were only six men of marriageable age. So, many French women started marrying men who were younger than them or men who belonged to lower classes. Both these practices have been considered taboo before the war.
So, in a way, the first world war changed the way marriages worked.
Women couldn’t find jobs
Until the 18th century, women were mostly housewives. Women who went to work either worked on farms or did small jobs like stitching. They did not work in factories. However, in the 18th century, when the industrial revolution started, women started working in factories (textile industries and coal mines).
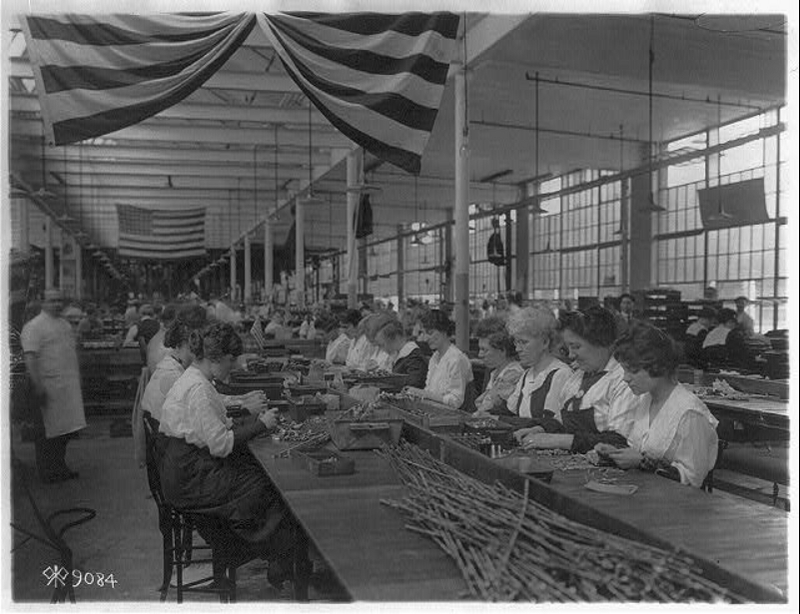
Due to the lack of men during the first world war, women entered the workforce in large numbers. They worked in industries, factories, and varied fields as teachers, secretaries, etc. They started wearing shorts, which changed clothing fashion tremendously. Due to their increasing importance in factories, women even got the right to vote.
However, once the war ended, everything changed for women. Men entered the workforce once again. As a result, many women had to give up their jobs. Most young women who had hoped to enter the workforce couldn’t find any jobs.
Those were hard times for single women. Many of them could neither find a man to marry nor a job to sustain themselves. Therefore, many single women became poor, finding it difficult even to feed themselves.
The Aftermath of World War 1 – A Summary:
The first world war was a devastating war in terms of the casualties it caused. Whether it be the countries that were created due to it or the economic and social changes that followed, the aftermath of world war 1 can still be felt all over the world.
The world tried to take all the precautions it could take to avoid another such war. Despite all those efforts, another war of even a greater scale would begin in the next two decades.
Even though it seemed that the world had learned from its mistakes, how did another war start? What are the conditions that led to it? Read more about it, in our blog post here:






Leave a Reply