Based on its year of creation, a piece of art or architecture can be classified as follows:
Stone age art (2,500,00 BC – 3000 BC)
Stone age art can be classified into Mesolithic art (10,000 BC – 4000 BC) and Neolithic art (4000 BC – 2000 BC).
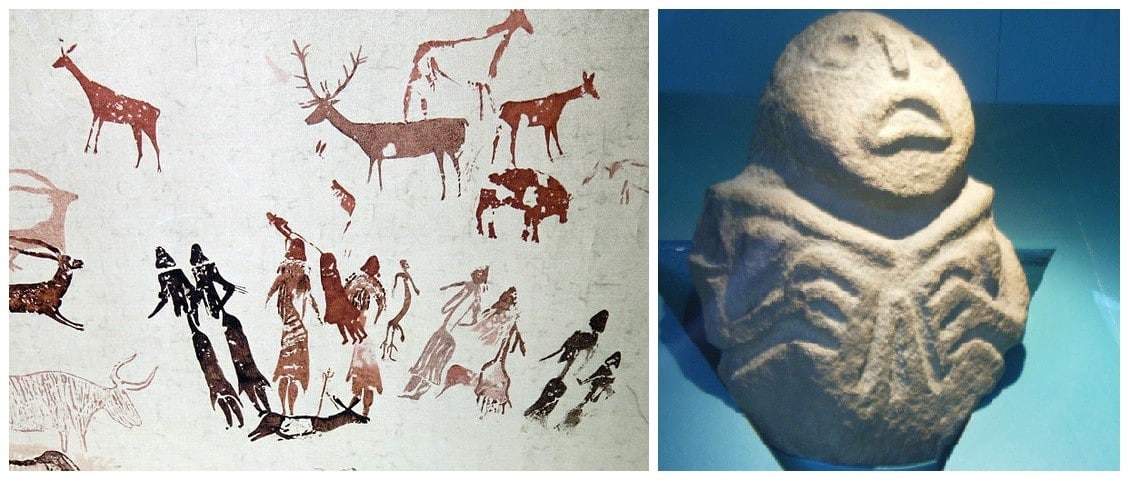
The paintings that were found before Mesolithic age are mostly cave paintings. These were mostly abstract or symbolic paintings. For example, the cave painting that can be found in Altamira cave, Spain was dated to be between 13,000 and 35,000 years old.
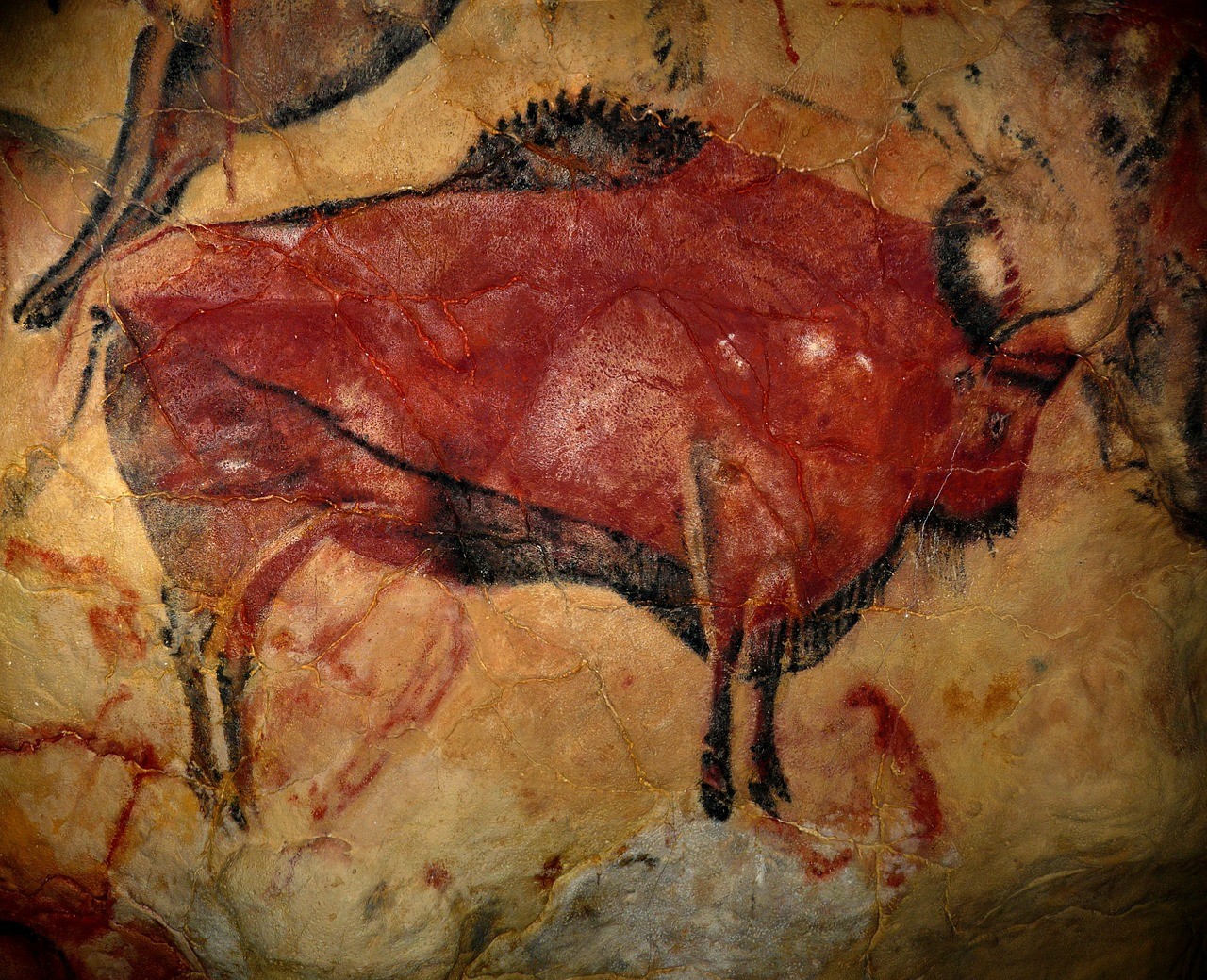

Cave Painting in Altamira
Mesolithic art (10,000 BC – 4000 BC)
Mesolithic art age began with the change in climate and an improvement in living conditions, which led to humans moving out of caves and living on outdoor sites. Hence, in the Mesolithic age, humans started to paint more on outdoor sites than caves.
Several paintings found from this era are human figures and the paintings started to become more narrative. This is also the era where 3D-art in the form of sculptures started to be carved. Decorative drawings on objects like Pots also started to emerge during this period.
One of the greatest works from this era is the “Thinker from Cernavado”.
Neolithic art (4000 BC – 2000 BC)
Due to the increased settlements and origin of civilizations, Neolithic age gave birth to crafts. Therefore, in the Neolithic age, due to the development in pottery and weaving, ornamentation and decoration attained more focus. It is during this period that calligraphy was invented in China.
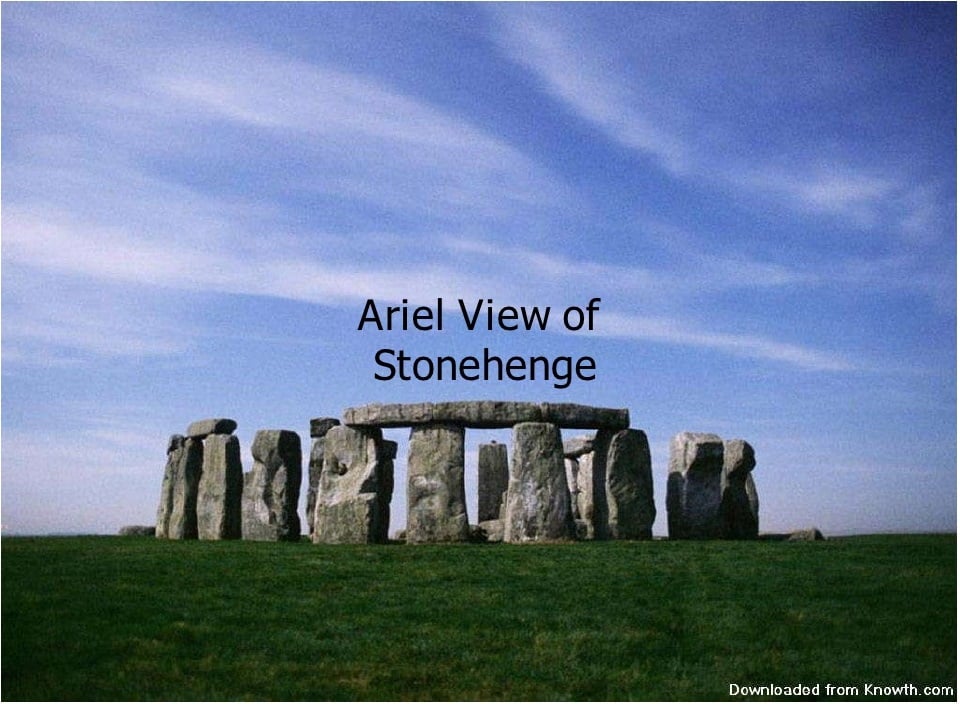
Primitive jewelry emerged during this era. This is not to say that art was completely ignored. Indeed art in the form of bronze statues and large-stone structures (megaliths, passage tombs and pyramids) became famous during this era. One of these famous large-stone structures is the Stonehenge, England.
However, ceramic pottery was the major medium of Neolithic art.
Bronze age art (3000 BC – 1200 BC)
Due to the emergence of cities, and the creation of more sophisticated tools, the bronze age gave rise to a wide range of monumental artworks. Some of the famous arts during this era include
Egyptian art
Burial chambers called pyramids and wax paintings were the masterpieces of the Egyptian art.
Persian art
Persian art was well-known for the ceramic paintings, carpets, silk weaving and rock sculptures.
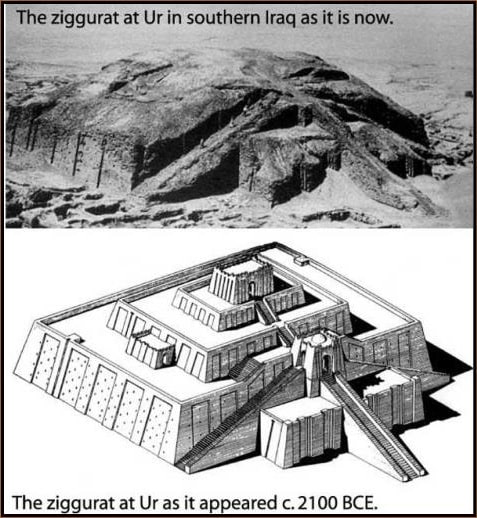
Sumerian art
Sumerian art is famous for the stepped pyramids called Ziggurats built from clay bricks and decorated with colored glazes.
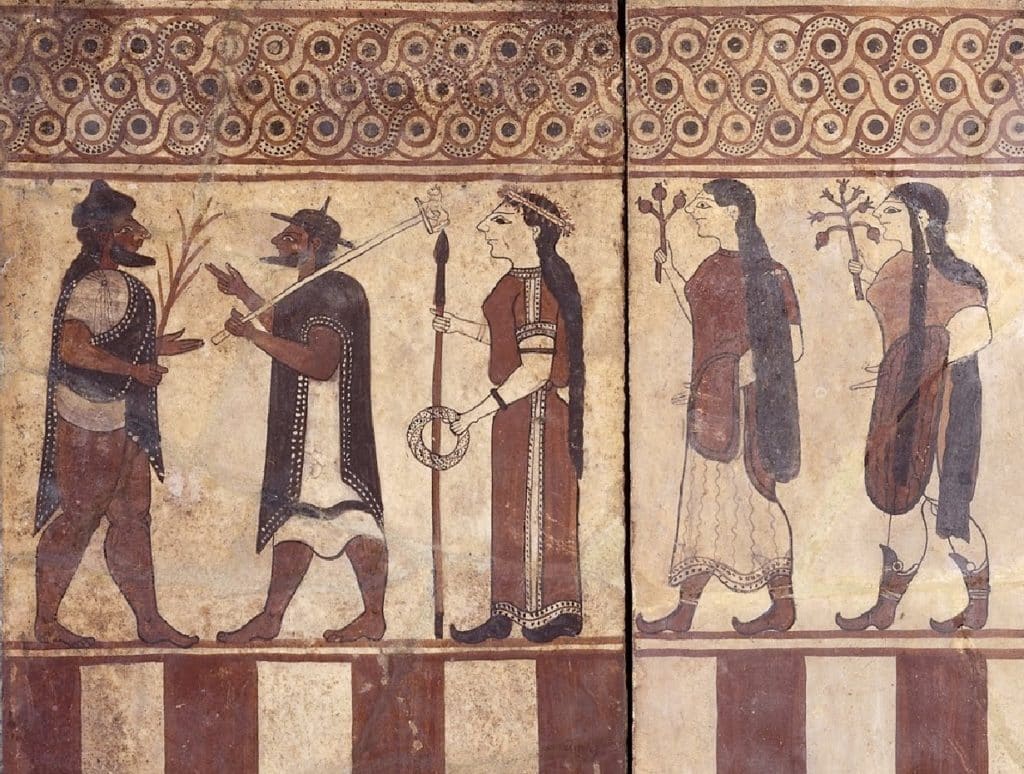
Minoan art
Minoan art often featured marine as well as mythological animals on stone, ceramics and vases.
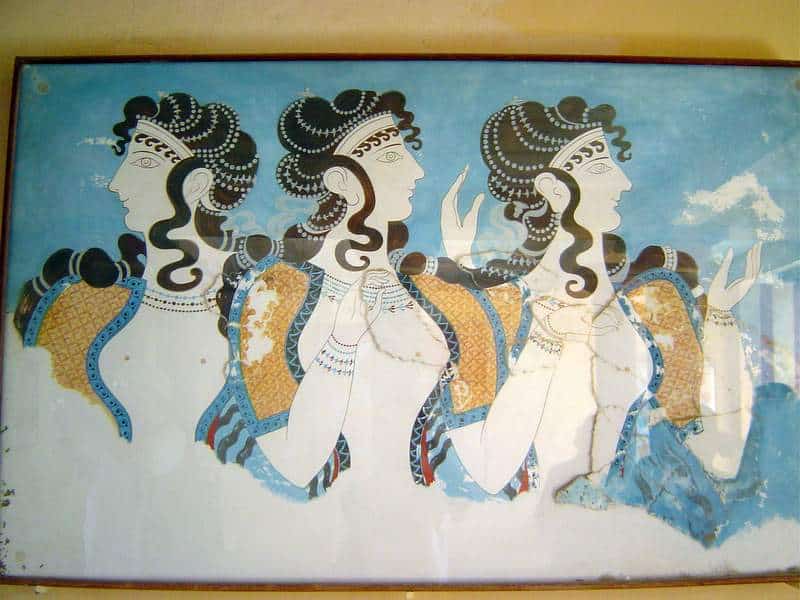

Picture credits - https://www.flickr.com/photos/cavorite/98591365/in/album-1011009/
Iron age art (1500 BC – 350 BC)
Due to the discovery of iron and the creation of iron tools of different shapes and sizes, metalwork as an art form started to flourish during this period. Only few secure cities existed during this era. Therefore, art was mostly limited to adornments on personal items, vessels, weapons and boats. Some of the famous arts of this era are:
Greek art
Greek art went through different ages maturing from paintings on pots and vases to paintings of important military and political successes to the construction of huge structures, which gave rise to some of the wonders of the ancient world.
Etruscan art
Etruscan art was famous for their tomb or funerary paintings.
Celtic art
Metalwork was the major form of Celtic artwork.
Roman art
Romans adapted the Greek art style to create paintings to glorify Rome`s power and build grandiose monuments to entertain their population.
Medieval art (350 BC – 1300 AD)
With the death of the Roman emperor Theodosius in 395 AD, Rome was split into two halves and Christianity became the official religion of the empire. Due to these advancements, medieval art was mostly themed around Christianity and Bible. Some of the noteworthy art styles of this era include:
Byzantine art
Almost entirely religious (Christianity), Byzantine art focused more on 2D-paintings in churches rather than 3D-sculptures.
Early Irish Christian art
Ornate manuscripts and religious metalwork, including crosses decorated with scenes of Bible were the iconic artworks of the Early Irish Christian art.
Romanesque art
Illuminated Christian texts depicted to the world, the beauty of the Romanesque art.
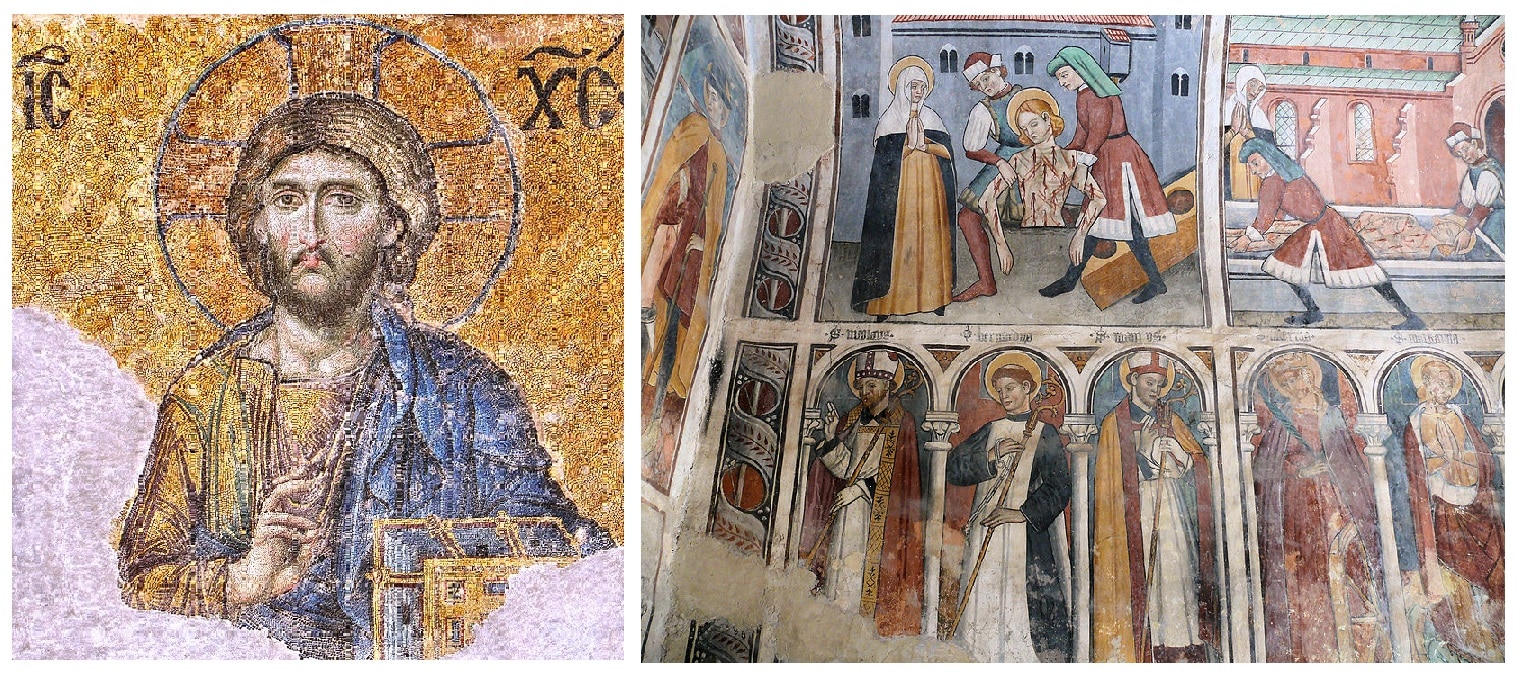

Byzantine art By Dianelos Georgoudis - Own work, CC BY-SA 3.0 & Gothic art By MOSSOT - Own work, CC BY-SA 3.0,
Gothic art
Stained glass art in cathedrals to tell the illiterate masses about the stories in the Bible are the masterpieces of Gothic art. Some famous examples include Notre Dame in Paris, the Cologne Cathedral and St Stephen`s cathedral in Vienna.
The Renaissance (1300 AD – 1620 AD)
While the Medieval art focused mostly on religious aspects, the Renaissance, centered on Italy, was the reestablishing of fine art painting and architecture based on the principles of Iron age Greek art.
Renaissance (1300 AD – 1620 AD)
Renaissance was built upon the idea of “Humanism”, which downplayed the religious domination of art to create art that was based on the dignity and worth of the individual. This was possible because of rich Italian families who started patronizing artists and funding them. Due to this new financial support, artists started rejecting the emphasis on religion (focus of medieval art) and started focusing more on the human aspect of life.
During this era, in northern Europe, oils started to be used for painting. Printmaking also gained popularity with the invention of printing press.
Mannerism (1525 AD -1600 AD)
Another form of art, called Mannerism (1525 AD -1600 AD), also developed during the end of this era as a response to Renaissance. It was more artificial and intellectual whereas Renaissance was more naturalistic.
Elongated human figures with varied emotions and strained poses, unusual variation in lighting (to create depth), scale, color or perspective are common attributes of art based on Mannerism.
Post Renaissance art (1600 AD – 1850 AD)
During this era, several types of art flourished in the following chronological order:
Baroque art (1600 AD – 1700 AD)
The Baroque is a highly extravagant style of art and architecture employed mostly by the churches to attract the masses.
The main characteristics of Baroque art was the heavy use of the primary colors (Yellow, Red and Blue), light and darkness to bring focus to the central figures.
Another main characteristic of Baroque architecture is the dome that had lavishly decorated paintings of angels and saints. This gave the impression of those looking from below as though they were looking up at heaven. Baroque paintings mostly brought back heroic moments in history back to life with the main motto being emotion, movement and drama.
Rococo art (1700 AD – 1789 AD)
Rococo art's main motto was to create a sense of awe and inspiration which was achieved not only by the simple exteriors and extravagant, theatrical interiors, but also by the use of curves, counter-curves and other elements modeled on nature.
Paintings were often integrated with carved, painted woodwork and gilded Bronze. Looking at the illusionist ceiling paintings often gave the impression that the figures on the dome were looking down at the people below.
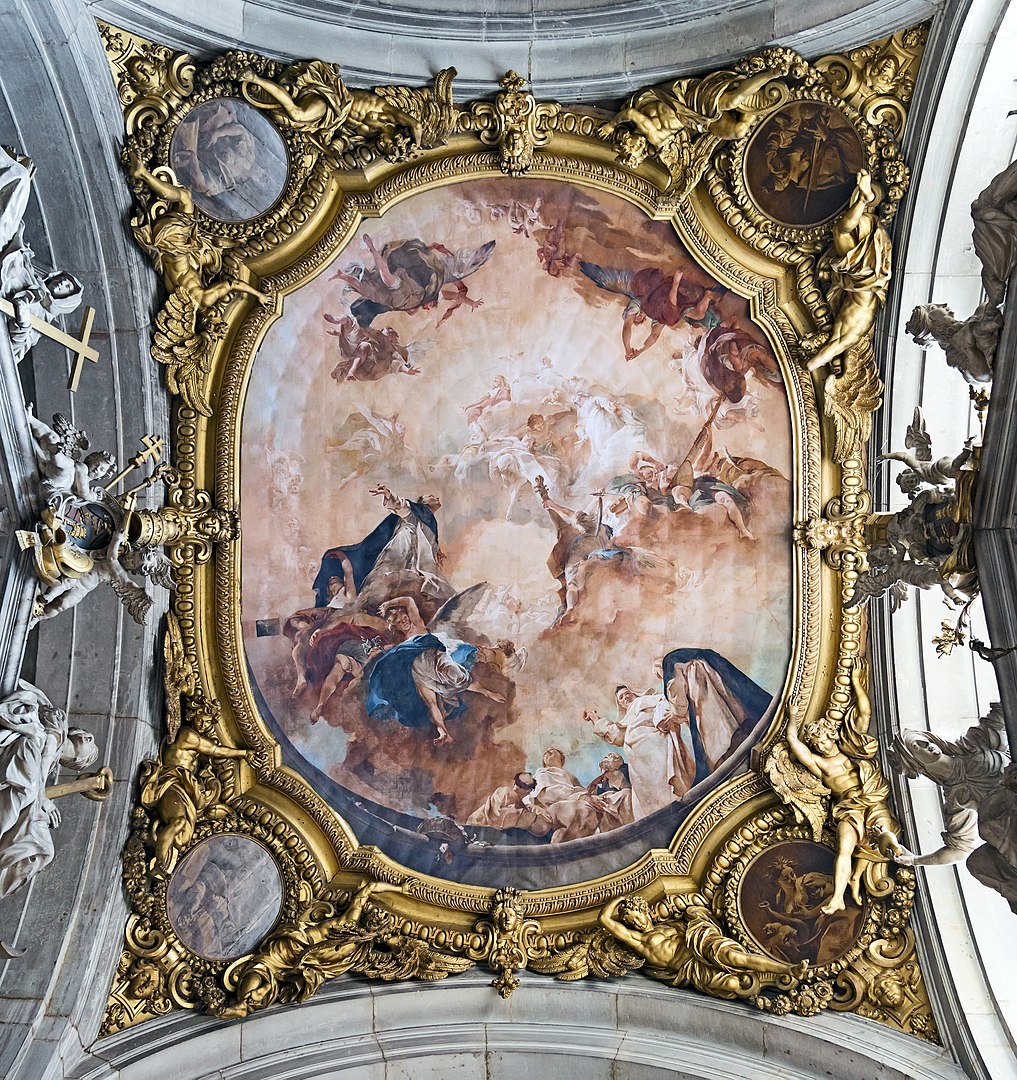

Interior of Santi Giovanni e Paolo (Venice) - The Glory of St. Dominic by Piazzetta
By Didier Descouens - Own work, Public Domain
Neoclassical art (1790 AD – 1830 AD)
Born as the response to the famous Rococo art, Neoclassical art is characterized by the renewed attachment to Greek and Roman mythology, paintings of heroic nude male, dramatic lighting and the use of White, Red and Gold colors.
The Romanticism movement (1790 AD – 1830 AD)
In stark contrast to Neoclassical art that focused on the intellectual and universal values (like heroism), Romanticism focused more on senses and emotions and glorified the past and nature.
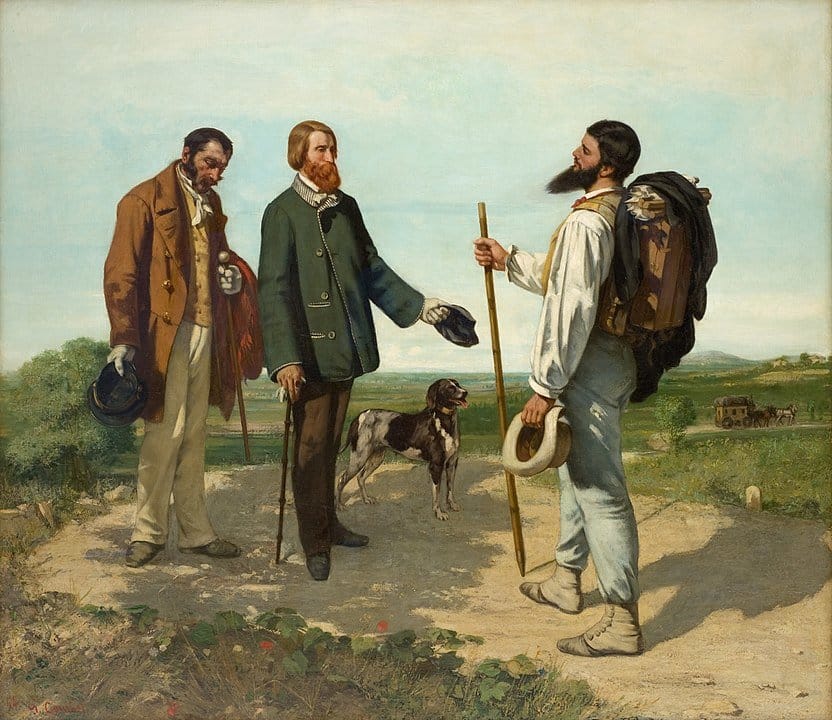
Realism
Realism is the art of depicting subject matter without adding any superficial elements like extra colors, supernatural elements, etc. It is also called Naturalism.
Due to the 1848 revolution, not just royal people, exaggerated emotions and supernatural elements, but also average, working class people and day-to-day happenings that happened in the present were seen as art-worthy subjects. This gave rise to Realism in the 1850s.
Modern art (1860s - 1970s)
The advent of industrial revolution changed the way people lived and traveled. This gave rise to crowded urban areas (market places and commuting areas), which where very good places for artists to showcase their talents.
Emergence of these crowded urban areas and social changes inspired artists to try new themes, thereby giving birth to a dozen types of art. The following are the most noteworthy among these art types.
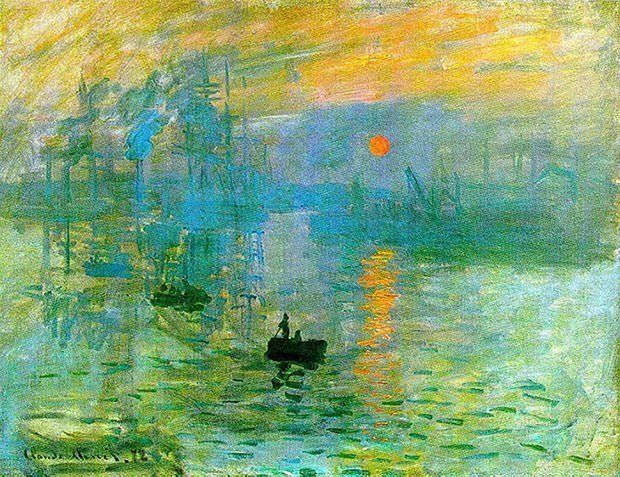
Impressionism
Characterized by loose brushwork and non-naturalist colors, most of the works of impressionism were landscapes. Many impressionist paintings will be unrecognizable, if looked close-up.
Fauvism
Fauvism is very similar to Impressionism in the way the paintings were made. It, however, made use of extravagant and varied colors that made Impressionist paintings look simple.
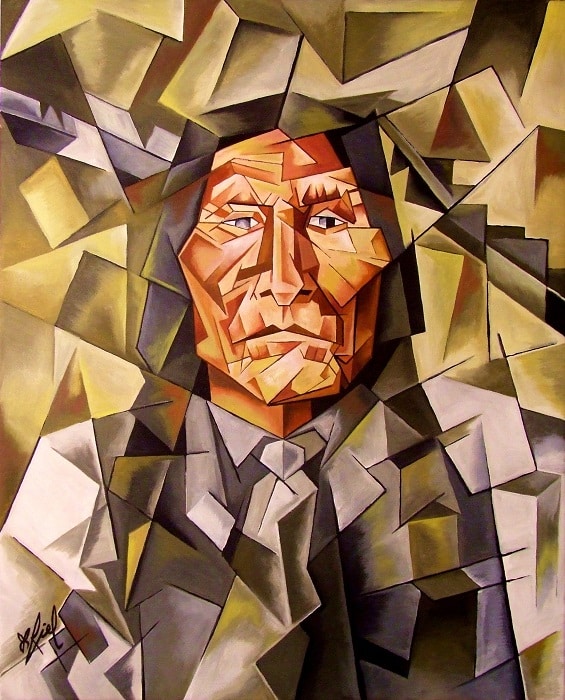
Cubism
Contrary to other methods of painting where lines were used to create images, flat planes were used in Cubism to create images and convey messages.
Futurism
Futurism glorified future technologies like machinery, airplanes and other scientific achievements.
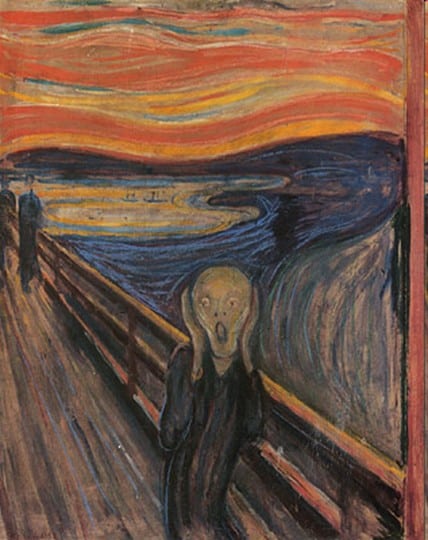
Expressionism
The main goal was to convey emotion rather than depict reality. Distorted objects and vivid, shocking colors are used to achieve the same.
Contemporary art (1970 AD - present)
In this era, the focus has shifted from the artwork itself to the message it conveys and how the artist conveys it. Hence, several medias like graffiti, video, etc have come into play.
Fun facts you probably didn't know
- Stone age humans created paintings and sculptures not for entertainment, but only because they thought that these paintings and sculptures have supernatural powers.
- Religion played a major part of daily life during the Medieval Ages, reasons why the artists of the early Medieval Ages were predominantly priests and monks who lived in monasteries.
- Anatomy was another interest to Renaissance artists. Artists worked with scientist in dissecting the human body to help them with proportions so that they could better themselves in depicting the true image of a human.
- There was a sculpture so small, its artist accidentally inhaled it.
We hope that this blog post on the history of art helped you understand how art has evolved over the years. If you liked this blog post, you will like the following blog post too: