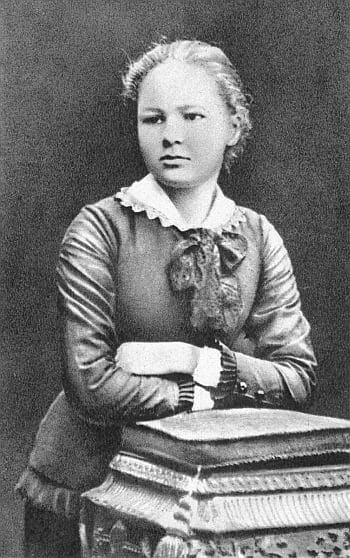Madame Marie Curie is an inspiration for women all over the world. This article will help you understand who Marie Curie is and what her achievements are. Finally, this article also lists some interesting facts about Marie Curie that everyone should know.
Who is Madame Marie Curie?
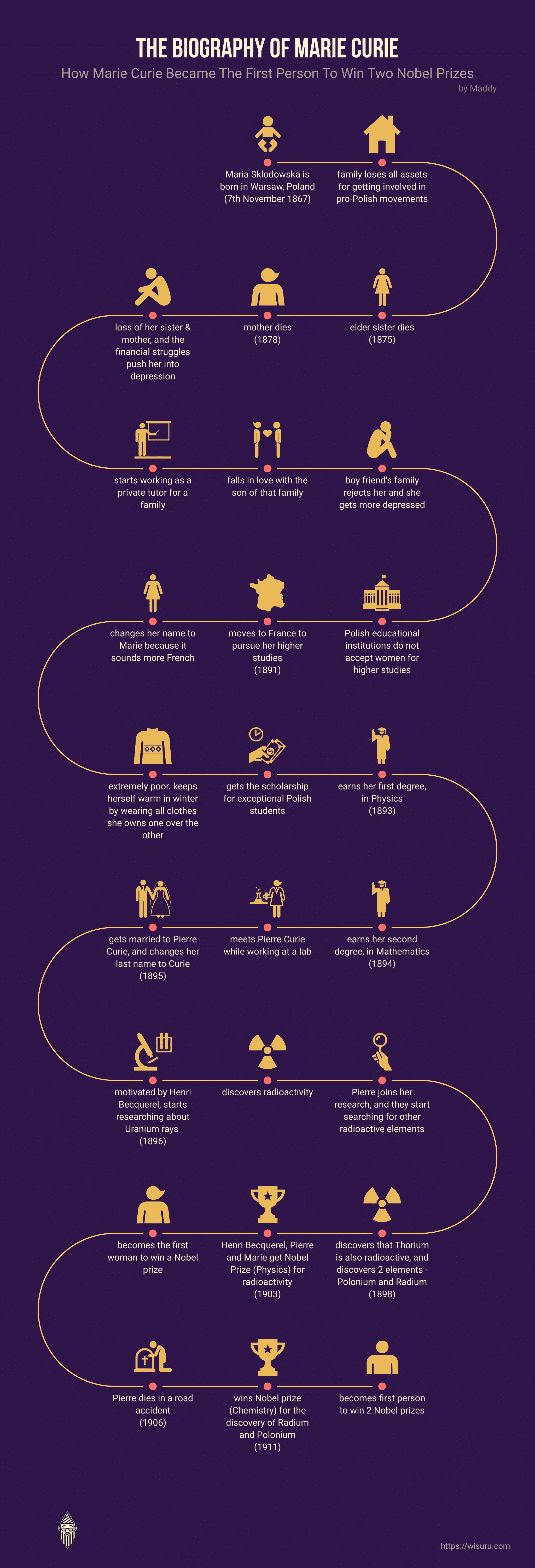
Madame Marie Curie was the first woman in history to win a Nobel prize. She is also the first person to win the Nobel prize twice. In an age where women were ridiculed for expressing their thoughts, she won not just one, but two Nobel prizes.
For decades, her research in the field of radioactivity and her discovery of two new elements has inspired young girls to take up a career in science.
Even though she became world-famous, in her younger years, Madame Marie Curie struggled financially and emotionally.
Read the story of a woman who, through pure passion and relentless hard work, overcame all her struggles in life and carved her name in history.
Birth
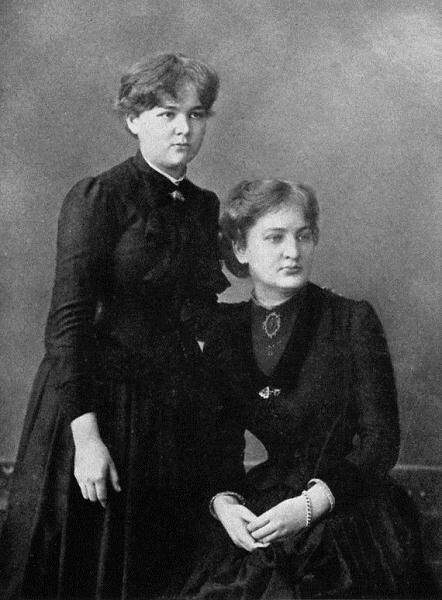
Maria Sklodowska was born in the city of Warsaw in Poland on 7th November 1867. One of the interesting facts about Marie Curie is that both her parents were successful in their respective fields. Her father was a teacher of Mathematics and Physics, and her mother was the head of the Warsaw boarding school for girls. Maria was their fifth and youngest child.
Childhood and depression
Maria saw a lot of struggles in her early years as their family lost all their assets for getting involved in patriotic pro-Polish movements. She suffered from depression since her teenage, probably because of the financial struggles and the loss of her mother and sister very early.
A failed love and more depression
During those days, educational institutions did not permit women to take up higher education. Hence, Maria tried to enroll in an underground educational enterprise to do her higher education.
She tried to raise necessary funds for her studies by working as a Governess (a private tutor for children) for a family, where she fell in love with their son. His parents did not support the relationship, and they were forced to part ways. This pushed Maria further into depression.

A Titbit About A GREAT Personality In Your Inbox Everyday
Find out how people changed our world and made history while doing it. Find out what motivated them to become their best self. Find out how they found innovative solutions to impossible problems.
Get a peek into the life of a great personality every day.
Passion helps overcome depression
Difficulty in collecting enough funds for her higher education did not deter Maria. Despite her depression, she continued to work as a governess to earn enough money to pay her tuition fees.
Those days, educational institutions in Poland did not let women enroll in courses. So, Maria decided to study on her own. Such was her passion for learning.
Finally, in 1891, Maria left Poland. She moved to France to pursue her higher education in an esteemed institution.
“I am among those who think that science has great beauty” -Madame Marie Curie (Source)
Financial struggles
When she moved to Paris, Maria registered herself as Marie, which sounded more French than Maria.
In France, her financial position was so bad that Marie did not even have enough clothes to wear during harsh winters. She only managed to keep herself warm by wearing all the clothes she owned one over the other. She studied in the morning at the university and earned little money by tutoring a few children in the evening.
Despite all her struggles, she was one of the best in her class. So, she got a scholarship which was only awarded to exceptional Polish students abroad.
Marie earned her first degree in Physics in 1893. With the help of the money from the scholarship and by working at an industrial laboratory in addition to her studies at the university, Marie earned her second degree in Mathematics a year later.
Meeting her future husband
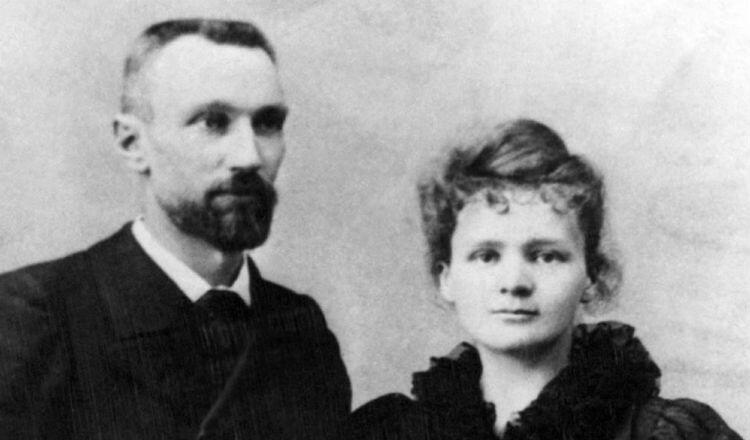
During her job, a Polish physicist introduced Marie to her future husband, Pierre Curie. The physicist hoped that Pierre could help Marie get a bigger laboratory space for her research.
Marie later quoted her first meeting with Pierre as follows:
“I was struck by the open expression of his face and by the slight suggestion of detachment in his whole attitude. His speech, rather slow and deliberate, his simplicity, and his smile, at once grave and youthful, inspired confidence.” - Marie Curie (source)
Within a year, Pierre proposed to Marie. However, Marie couldn’t accept it because she wanted to go back to Poland for work. However, the Kraków university denied her a job because she is a woman. So, she came back to Paris to pursue her Ph.D. In 1895, Pierre Curie completed his Ph.D. The same year, they both got married in a simple manner.
After marriage, she changed her name to Marie Curie after her husband’s name, Pierre Curie. After the birth of their daughter in 1897, Marie took up teaching in addition to her research to support her family.
Research
Inspired by Wilhelm Roentgen’s discovery of X-rays, Henri Becquerel was studying its properties using naturally fluorescent materials in 1896. While observing its behavior under a magnetic field, he found that Uranium emits rays that are different from X-rays.
This motivated Marie to pursue her research in the field of uranium rays and their electromagnetic properties.
When Curie experimented on uranium rays, she found that uranium rays remained constant regardless of the form of Uranium. Hence, these rays must have come from Uranium’s atomic structure. To describe this phenomenon, she coined the term ‘Radioactivity.’ Marie’s study on radioactivity gave birth to a new field of physics called Atomic physics.
Marie’s husband joins her research
By this time, her husband, Pierre Curie, was very impressed and intrigued by her research. So, he decided to drop his research and help her in her discovery.
Marie worked with two minerals of Uranium. She also sampled tonnes of the ore Pitchblende to understand more about its radioactive properties. She and Pierre began searching for other elements that are radioactive. In the year 1898, they discovered that the element Thorium was also radioactive.
Marie presented a brief paper on her discovery in the year 1898 since she knew that sharing her discovery with the world as early as possible was necessary to establish her predominance as an important woman scientist.
After years of extensive research, Marie and Pierre discovered two radioactive elements that they named “Polonium” and “Radium”.
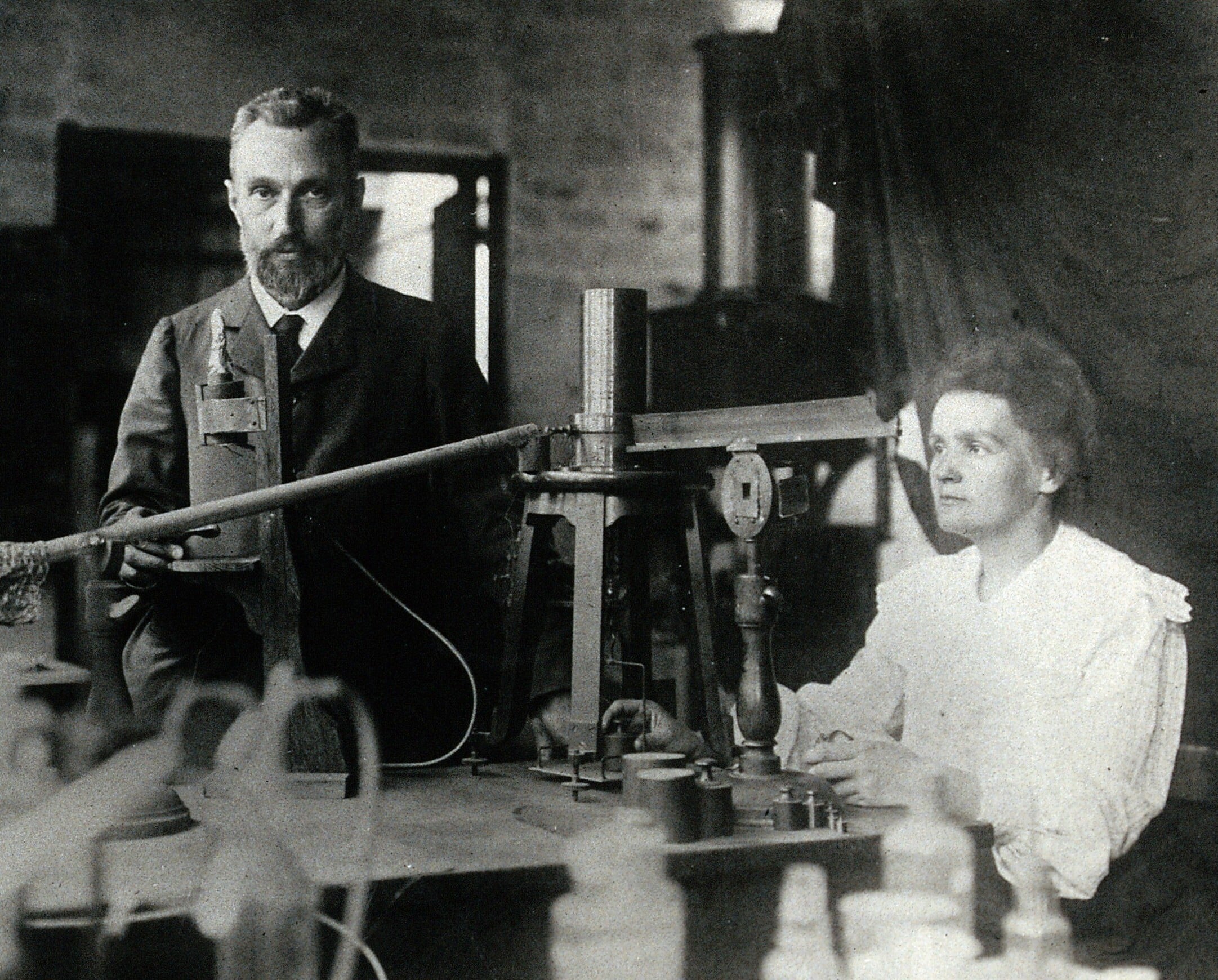

Marie and Pierrie in their laboratory, 1904 - By Unknown author - hp.ujf.cas.cz (uploader=--Kuebi 18:28, 10 April 2007 (UTC)), Public Domain, Link
Unfortunately, Pierre Curie died in a road accident in the year 1906. After his death, Madame Curie continued her research on radioactivity. She isolated the element Radium in 1910 and devised an international standard to measure radioactivity.
Winning the Nobel prizes
In 1903, Henri Becquerel, Pierre Curia, and Marie Curie were awarded (together) the Nobel prize for Physics for their work on radioactivity.

A picture of the 1903 Nobel Diploma for Physics - By Dannybalanta2011-04-16 / Public domain
In the year 1911, she won her second Nobel prize, in Chemistry, for the discovery of Radium and Polonium.

A picture of the 1911 Nobel Diploma for Chemistry - By Nobel Foundation - Unknown source, Public Domain, Link
Marie’s research continues
Marie continued her research for years to come. She was conferred with many national and international honors by different universities and institutions for her path-breaking research. She also lent her services and research into the field of medicine.
Marie also served as a radiologist in hospitals during World War 1. She invented the first mobile x-ray machine that helped doctors understand the internal damage in soldiers hurt during the war. She even drove the ambulances equipped with x-rays machines to provide service during the war.
Death
One of the interesting facts about Marie Curie is that her love for science eventually killed her.
Marie Curie and Pierre Curie were conducting their research in a very poorly ventilated shed near their home. They did not know the disadvantages of working with strong metals in a poorly ventilated space. As a result, her continuous exposure to radiations caused Aplastic anemia, which ultimately killed her in the year 1934.
She was buried in a cemetery beside her husband. The remains were transferred to the Pantheon in Paris in the year 1995 to honor their discoveries and achievements.
Marie’s contribution to the world
If put simply, Marie Curie changed the course of science forever with her discoveries and research. Her determined resolve helped us understand more about radioactivity and how it can be used in various forms. She basically taught us that atoms are, in fact, divisible and consist of smaller subatomic particles.
Her discovery of the two radioactive elements and research on the properties of these elements gave us the process of carbon dating, as we know today. Carbon dating is the method by which we calculate the earth’s age and of all its fossils. To this day, She continues to be an inspiration for women in the fields of science.
Marie and Pierre refused to make money from their discoveries. So, they did not file for a patent after they discovered Radium in 1898. This is one of the interesting facts about Marie curie.
“Marie Curie is, of all celebrated beings, the only one whom fame has not corrupted” - Albert Einstein (source)
Today, Radium, is used widely in the medical field. It is used for controlling cancer growth using radon gas in radiotherapy. These elements are also used in nuclear reactors to produce atomic energy as well.
The research institutes that Marie founded are known as the Curie institutes. They are very prominent research centers for scientists and perform extensive medical research even today.
Marie used the money from the Nobel prize to fund her research and help others.
Interesting Facts about Marie Curie
Here are some interesting facts about Marie Curie that everyone should know.
- Marie Curie was originally ignored in her race for a Nobel Peace prize. The committee was reluctant to give a woman an award and wanted to give it to her husband in stead. Pierre Curie, in turn, asked the Nobel Committee to consider their submission as a joint submission only.
- In 1911, Marie was embroiled in a controversy of having an affair with a former student of Pierre Curie. It was during this time when Marie was comforted by Albert Einstein. Then, she ignored the controversy and continued to work diligently on her discoveries.
- Till date, Marie remains the only Nobel laureate to win Nobel prizes in two separate sciences. She also has a hospital named after her in London, which treats female cancer patients.
- She spent years in her research and also cut on her family time to complete her research. For her wedding, she chose to wear a dark blue dress, instead of a bridal gown. When questioned, she replied, “I have no dress except the one I wear every day. If you are going to be kind enough to give me one, please let it be practical and dark so that I can put it on afterward to go to the laboratory.” - Source
- In the 1920s, Radium became too costly (1 gram cost $100,000). So, even though Marie invented the element since she didn’t patent it, she didn’t have enough money to procure it for further research.
- In 1935, her daughter and her husband won the Nobel prize in Chemistry for their discovery of artificial radioactivity. Her other son-in-law collected the Nobel prize for peace on behalf of UNICEF. This makes Curies’ family the family with the highest number of Nobel prizes.